For a
molecule that is lack of C-H bonds, less information is forthcoming. For
examples, polychlorinated compounds, polycarbonyl compounds, and
compounds containing triple bonds.
Why did 13C-NMR spectroscopy is developed after 1H-NMR spectroscopy?
13C-NMR spectroscopy was developed after 1H-NMR spectroscopy because
However, development of FTNMR techniques helps 13C-NMR spectroscopy become widely available because
Normal range of 13C chemical shift is 0 - 220 ppm (dC » 20 x dH).
The correlation chart of 13C chemical shift list in ppm from a referent compound, TMS
| 1. saturated C atoms appear at highest field (8 - 60 ppm) 2. saturated C atoms with EN effects appear in the range of 40 -80 ppm 3. unsaturated C atoms (alkenes, alkynes, aromatic compounds) appear in the range of 100- 175 ppm 4. carbonyl C atoms appear in the range of 155 - 220 ppm |
|
| Like in 1H chemical shifts, 13C chemical shifts can be affected by EN and hybridization. | |
- the electronegative atom is directly attached to C atom and - the effect occurs through only one bond (C-X). In the other hand, H is attached to C atom not directly to the electronegative atom so the effect occurs through only one bond (H-C-X). |
|
The amount of 13C in a molecule is very small. Therefore, the chances of two adjacent carbon atoms being both 13C are very small. For this reason, homonuclear (C-C) coupling is rarely observed.
Proton-coupled 13C splitting patterns
Spectra which show the spin-spin splitting between 13C and the protons directly attached to it are called proton-coupled spectra or nondecoupled spectra.
The figure below shows the proton-coupled 13C NMR spectrum for ethyl phenylacetate. Although the alkyl carbon peaks are widely separated in this example, in more complicated structures the alkyl portion of the spectrum can be very difficult to interpret.
Proton-coupled 13C spectra for ethyl phenylacetate
Example : 13C-NMR spectrum of diethyl phthalate
Proton-coupled spectra are often difficult to interpret because
1. Js for 13C-H couplings are between 100 to 250 Hz. 13C-H coupling constants are frequently larger than the d differences of the carbons in the spectrum.
2. 13C normal signals with 1H coupling has low signal/noise ratio due to the multiplet structure.
Click here to see more details about NOE
Double-Resonance Experiments
| |
Identifying structure from proton-coupled spectra may difficult because peak overlap. Broad-band decoupling technique is developed to solve this problem. |
| Principle of broad-band decoupling (BB) : | |
| |
The decoupling process is accomphished by irradiating the sample with a broad spectrum of high intensity RF radiation between 40 -70 MHz while scanning at normal intensities at frequencies about 15 MHz. All protons become saturated and can no longer couple with 13C nuclei. |
A. The Proton-coupled 13C NMR spectrum
B. The BB-decoupled 13C NMR spectrum : each carbon atom gives a single signal (multiplicity is lost).
Example 2: 22.63 MHz 13C NMR spectra of crotonic acid in CDCl3
a) spectrum with proton-coupling
|
b) spectrum with 1H broad-band (BB) decoupling
|
Example 3: The 13C-NMR spectrum of 1-chloro-2-propanol
| This 3-C containing compound shows well separated peaks because they are different in shielding effects caused by circulating electrons. | |
| The lower electron density at the carbon, the less shielded, and the more downfield signal. | |
| For this reason, the carbon bearing the -OH group is the most deshielded carbon and shows the furthest downfield signal at d 67. | |
| Chlorine is less electronegative than oxygen and the carbon bonded to it gives more upfield signal at d 51. | |
| The methyl carbon (-CH3) has no electronegative groups attached, so it occurs the most upfield at d 20. |
Example 4: 13C-NMR spectrum of diethyl phthalate
Advantages of BB-decoupling:
 clarify of the chemical shift difference among carbon signals
clarify of the chemical shift difference among carbon signals
 increasing of signal intensity of 13C signals (up to 200%)
increasing of signal intensity of 13C signals (up to 200%)
 short recording time
short recording time
Disadvantages of BB-decoupling:
 lost of coupling information (s, d, t, and q)
lost of coupling information (s, d, t, and q)
| Although broad-band decoupled spectra are much simple, important information may be lost, that is the number of attached hydrogen atoms. A more advanced technique, off-resonance decoupling, can restore this information while still presenting an easily interpretation. | |
| In this technique, the sample is irradiated by a radio frequency generator which is either slightly upfield or downfield of normal proton resonances (i.e., off resonance). When off-resonance decoupling is used, the apparent coupling constant is greatly reduced, and peak overlap is minimized. | |
| Off-resonance spectra often show only singlets for each carbon atom, but the multiplicity of the peak is reported as a letter (s , d, t, or q) above the peak. | |
Example 2: 13C-NMR spectrum of diethyl phthalate
Advantages of Off-Resonance Spectra
 determine the number of types of carbon in a molecule
determine the number of types of carbon in a molecule
 clarify of the chemical shift
clarify of the chemical shift
 retain multiplicities with reducing of J
retain multiplicities with reducing of J
Disadvantage of Off-Resonance Spectra
 if signals are closed, spectrum may be higher order and difficult to interpret
if signals are closed, spectrum may be higher order and difficult to interpret
Proton – coupled 13C-NMR spectra are often difficult to interpret due to large coupling constants and overlaping of signals. For this reason, 13C-NMR spectra are taken with proton–decoupled mode in which C/H ratios is lost.
To provide this information while retaining signal strength, DEPT (Distortionless Enhancement by Polarization Transfer) is developed.
In
DEPT experiments, methyl, methylene, and methine protons can be
distinguishable. There are several variations on the experiment.
sub-spectrum
|
technique
|
CH
|
DEPT 90o
|
CH2
|
DEPT 45o - DEPT 135o
|
CH3
|
DEPT 45o + DEPT 135o - 0.707DEPT 90o
|
C
|
comparing the DEPT with the BB decoupled spectrum
|
The types of carbon observed with various of DEPTs.
| 1. | DEPT 45o | |
| 2. | DEPT 90o | |
| 3. | DEPT 135o |
Nomally, only two DEPT experiments are sufficient, DEPT 90o and DEPT 135o.
| - there is no signal of C with no attached H - CH2 shows negative signal whereas CH and CH3 show positive signal - CH carbons absorb at lower field and lower signal intensity than CH3carbons |
Example 1: DEPT spectrum of isobutyl acetate
Interpretation :
d (ppm)
|
type of signal in DEPT
|
represent
|
22 (b)
|
positive
|
2 CH3
|
24 (c)
|
positive
|
CH3
|
24 (a)
|
positive
|
CH
|
37 (d)
|
negative
|
CH2
|
62 (e)
|
negative
|
CH2
|
170 (f)
|
not present
|
C of >C=O
|
Example 2: DEPT spectrum of caryophyllene oxide
بقري، وتعلم معي، قطرات صغيرة من الماء جعلالمحيطات، وسوف يكون خبيرا في هذا
what is this, why are you worried, brush up with simple things, you will come out genius, learn with me, small drops of water make an ocean, you will be an expert in this
あなたが心配している理由は、これは簡単なことでブラッシュアップ、、何か、あなたは、天才が出てくる私と一緒に学ぶことが、水の小さな滴が海を作るには、この専門家になる
Name: 1,2-dimethoxymethane
C4H10O2
From the molecular formula, the compound has "0 degrees of unsaturation" (no double bonds or rings).
The 13C NMR has two peaks, a quartet at  54 (a CH3) and a triplet at
54 (a CH3) and a triplet at  80 (a CH2). Since the molecule has four carbons and only two 13C NMR peaks, there must be symmetry. Both peaks are in the regions where carbons next to electronegative atoms occur (oxygen).
80 (a CH2). Since the molecule has four carbons and only two 13C NMR peaks, there must be symmetry. Both peaks are in the regions where carbons next to electronegative atoms occur (oxygen).
 54 (a CH3) and a triplet at
54 (a CH3) and a triplet at  80 (a CH2). Since the molecule has four carbons and only two 13C NMR peaks, there must be symmetry. Both peaks are in the regions where carbons next to electronegative atoms occur (oxygen).
80 (a CH2). Since the molecule has four carbons and only two 13C NMR peaks, there must be symmetry. Both peaks are in the regions where carbons next to electronegative atoms occur (oxygen).
τι είναι αυτό, γιατί είσαι ανήσυχος, βούρτσα με απλά πράγματα, θα βγει ιδιοφυΐα, να μάθουν μαζί μου, μικρές σταγόνες του νερού κάνει έναν ωκεανό, θα είστε ένας εμπειρογνώμονας σε αυτό
আপনি চিন্তিত কেন এই সহজ জিনিস নিয়ে ব্রাশ,, কি, আপনি, প্রতিভা বাইরে আসতে আমার সাথে শিখতে হবে, জলের ছোট ঝরিয়া একটি মহাসাগর না, আপনি এই একজন বিশেষজ্ঞ হতে হবে
C5H7O2N
From the molecular formula, the compound has "3 degrees of unsaturation" (3 double bonds or rings).
: ethyl cyanoacetate
The 13C NMR has 5 peaks, a quartet at  14 (a CH3), a triplet at
14 (a CH3), a triplet at  59 (a CH2), another triplet at
59 (a CH2), another triplet at  22 (another CH2), and two singlets, one at
22 (another CH2), and two singlets, one at  118 and one at
118 and one at  172. Since the molecule has five carbons and five 13C NMR peaks, there must be no symmetry. The singlet at
172. Since the molecule has five carbons and five 13C NMR peaks, there must be no symmetry. The singlet at  172 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an acid or an ester. The CH2 at
172 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an acid or an ester. The CH2 at  59 is in the region where carbons next to electronegative atoms occur (i.e., oxygen) and the CH3 at
59 is in the region where carbons next to electronegative atoms occur (i.e., oxygen) and the CH3 at  14 is a simple terminal methyl, suggesting an -O-CH2CH3 residue. The singlet at
14 is a simple terminal methyl, suggesting an -O-CH2CH3 residue. The singlet at  118 would be consistent with a nitrile carbon and the shielded CH2 at
118 would be consistent with a nitrile carbon and the shielded CH2 at  22 suggests that it may be adjacent to the sp-carbon of the nitrile
22 suggests that it may be adjacent to the sp-carbon of the nitrile
 14 (a CH3), a triplet at
14 (a CH3), a triplet at  59 (a CH2), another triplet at
59 (a CH2), another triplet at  22 (another CH2), and two singlets, one at
22 (another CH2), and two singlets, one at  118 and one at
118 and one at  172. Since the molecule has five carbons and five 13C NMR peaks, there must be no symmetry. The singlet at
172. Since the molecule has five carbons and five 13C NMR peaks, there must be no symmetry. The singlet at  172 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an acid or an ester. The CH2 at
172 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an acid or an ester. The CH2 at  59 is in the region where carbons next to electronegative atoms occur (i.e., oxygen) and the CH3 at
59 is in the region where carbons next to electronegative atoms occur (i.e., oxygen) and the CH3 at  14 is a simple terminal methyl, suggesting an -O-CH2CH3 residue. The singlet at
14 is a simple terminal methyl, suggesting an -O-CH2CH3 residue. The singlet at  118 would be consistent with a nitrile carbon and the shielded CH2 at
118 would be consistent with a nitrile carbon and the shielded CH2 at  22 suggests that it may be adjacent to the sp-carbon of the nitrile
22 suggests that it may be adjacent to the sp-carbon of the nitrile
מה זה, למה אתה מודאג, לרענן עם דברים פשוטים, אתה תצא גאון, ללמוד איתי, טיפות קטנות של מיםיגרמו לים, אתה תהיה מומחה בזה
C6H10OFrom the molecular formula, the compound has "2 degrees of unsaturation" (2 double bonds or rings).
2-butanon-4-ene
The 13C NMR has 6 peaks, a quartet at  25 (a CH3), a triplet at
25 (a CH3), a triplet at  49 (a CH2), another quartet at
49 (a CH2), another quartet at  17 (another CH3), two doublets (a CH) , one at
17 (another CH3), two doublets (a CH) , one at  124 and one at
124 and one at  131, and one singlet at
131, and one singlet at  207. Since the molecule has six carbons and six 13C NMR peaks, there must be no symmetry. The singlet at
207. Since the molecule has six carbons and six 13C NMR peaks, there must be no symmetry. The singlet at  207 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an aldehyde or ketone. The CH3 groups at
207 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an aldehyde or ketone. The CH3 groups at  17 and 25 are consistent with simple terminal methyl groups, with one slightly shifted by an mildly electronegative group (a carbonyl?). The doublets at
17 and 25 are consistent with simple terminal methyl groups, with one slightly shifted by an mildly electronegative group (a carbonyl?). The doublets at  124 and 131 are in the alkene region, suggesting a -CH
124 and 131 are in the alkene region, suggesting a -CH CH- group. The remaining CH2 group at
CH- group. The remaining CH2 group at  49 is probably deshielded by two electronegative groups.
49 is probably deshielded by two electronegative groups.
 25 (a CH3), a triplet at
25 (a CH3), a triplet at  49 (a CH2), another quartet at
49 (a CH2), another quartet at  17 (another CH3), two doublets (a CH) , one at
17 (another CH3), two doublets (a CH) , one at  124 and one at
124 and one at  131, and one singlet at
131, and one singlet at  207. Since the molecule has six carbons and six 13C NMR peaks, there must be no symmetry. The singlet at
207. Since the molecule has six carbons and six 13C NMR peaks, there must be no symmetry. The singlet at  207 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an aldehyde or ketone. The CH3 groups at
207 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an aldehyde or ketone. The CH3 groups at  17 and 25 are consistent with simple terminal methyl groups, with one slightly shifted by an mildly electronegative group (a carbonyl?). The doublets at
17 and 25 are consistent with simple terminal methyl groups, with one slightly shifted by an mildly electronegative group (a carbonyl?). The doublets at  124 and 131 are in the alkene region, suggesting a -CH
124 and 131 are in the alkene region, suggesting a -CH CH- group. The remaining CH2 group at
CH- group. The remaining CH2 group at  49 is probably deshielded by two electronegative groups.
49 is probably deshielded by two electronegative groups.
o que é isso, por que você está preocupado, retocar com coisas simples, você vai sair gênio, aprender comigo, pequenas gotas de água fazem um oceano, você vai ser um especialista neste
C8H8O
From the molecular formula, the compound has "5 degrees of unsaturation" (5 double bonds or rings).
acetophenone
The 13C NMR has 6 peaks, a quartet at  27 (a CH3), three doublets (CH groups), at
27 (a CH3), three doublets (CH groups), at  129, 128 and 133, and two singlets, one at
129, 128 and 133, and two singlets, one at  137 and one at
137 and one at  197. Since the molecule has eight carbons and six 13C NMR peaks, there must some degree of symmetry. The singlet at
197. Since the molecule has eight carbons and six 13C NMR peaks, there must some degree of symmetry. The singlet at  197 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an aldehyde or ketone. The CH3 groups at
197 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an aldehyde or ketone. The CH3 groups at  27 is consistent with a simple terminal methyl group, slightly shifted by an mildly electronegative group (a carbonyl?). The doublets at
27 is consistent with a simple terminal methyl group, slightly shifted by an mildly electronegative group (a carbonyl?). The doublets at  129, 128 and 133 and the singlet at
129, 128 and 133 and the singlet at  137 are in the aromatic region, suggesting a monosubstituted aromatic group, with symmetry in four of the six carbons.
137 are in the aromatic region, suggesting a monosubstituted aromatic group, with symmetry in four of the six carbons.
 27 (a CH3), three doublets (CH groups), at
27 (a CH3), three doublets (CH groups), at  129, 128 and 133, and two singlets, one at
129, 128 and 133, and two singlets, one at  137 and one at
137 and one at  197. Since the molecule has eight carbons and six 13C NMR peaks, there must some degree of symmetry. The singlet at
197. Since the molecule has eight carbons and six 13C NMR peaks, there must some degree of symmetry. The singlet at  197 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an aldehyde or ketone. The CH3 groups at
197 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an aldehyde or ketone. The CH3 groups at  27 is consistent with a simple terminal methyl group, slightly shifted by an mildly electronegative group (a carbonyl?). The doublets at
27 is consistent with a simple terminal methyl group, slightly shifted by an mildly electronegative group (a carbonyl?). The doublets at  129, 128 and 133 and the singlet at
129, 128 and 133 and the singlet at  137 are in the aromatic region, suggesting a monosubstituted aromatic group, with symmetry in four of the six carbons.
137 are in the aromatic region, suggesting a monosubstituted aromatic group, with symmetry in four of the six carbons.
நீங்கள் கவலை ஏன் இந்த எளிய பொருட்களை கொண்டு துலக்க, என்ன, நீங்கள், மேதை வெளியே வர எனக்கு கற்று, நீர் சிறு துளிகள் ஒரு கடல் செய்ய, நீங்கள் இந்த ஒரு நிபுணர் இருக்கும்
के तपाईं चिंतित हो किन यो सरल कुरा संग ब्रश,, के हो, तपाईं, प्रतिभा बाहिर आउन मलाई संग सिक्न हुनेछ, पानी सानो थोपा एक महासागर बनाउन, तपाईं यस मा एक विशेषज्ञ हुनेछ\
તમને ચિંતા થતી હોય કે શા માટે આ સરળ બાબતો સાથે બ્રશ, શું છે, તમે પ્રતિભા બહાર આવે મારી સાથે શીખશે, પાણી નાના ટીપાં સમુદ્ર કરો, તો તમે આ એક નિષ્ણાત હશે
kas tas ir, kāpēc jūs uztraucaties, suka ar vienkāršām lietām, jūs iznākt ģēnijs, mācīties kopā ar mani, nelieli ūdens pilieni veikt okeānu, jums būs eksperts šajā
что это такое, почему ты беспокоишься, освежить с простых вещей, вы будете выходить гений, узнать со мной, маленькие капли воды сделать океан, вы будете экспертом в этом
hvað er þetta, af hverju ert þú áhyggjur, bursta upp með einföldum hlutum, verður þú að koma út snillingur, læra með mér, litla dropa af vatni gera haf, verður þú að vera sérfræðingur í þessu
C6H8OFrom the molecular formula, the compound has "3 degrees of unsaturation" (3 double bonds or rings).

cyclohexanon-2-ene
cyclohexanon-2-ene
The 13C NMR has 6 peaks, three triplets (CH2 groups) at  46, 30 and 41, two doublets (CH groups), at
46, 30 and 41, two doublets (CH groups), at  129 and 145, and one singlet at
129 and 145, and one singlet at  198. Since the molecule has six carbons and six 13C NMR peaks, there must be no symmetry. The singlet at
198. Since the molecule has six carbons and six 13C NMR peaks, there must be no symmetry. The singlet at  198 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an aldehyde or ketone. Two of the three CH2 groups are shifted by electronegative groups, suggesting a X-CH2-CH2-CH2-Y unit. The doublets at
198 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an aldehyde or ketone. Two of the three CH2 groups are shifted by electronegative groups, suggesting a X-CH2-CH2-CH2-Y unit. The doublets at  129 and 145 are in the alkene region, suggesting a -CH
129 and 145 are in the alkene region, suggesting a -CH CH- group. The three degrees of unsaturation suggests that the molecule also has a ring.
CH- group. The three degrees of unsaturation suggests that the molecule also has a ring.
 46, 30 and 41, two doublets (CH groups), at
46, 30 and 41, two doublets (CH groups), at  129 and 145, and one singlet at
129 and 145, and one singlet at  198. Since the molecule has six carbons and six 13C NMR peaks, there must be no symmetry. The singlet at
198. Since the molecule has six carbons and six 13C NMR peaks, there must be no symmetry. The singlet at  198 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an aldehyde or ketone. Two of the three CH2 groups are shifted by electronegative groups, suggesting a X-CH2-CH2-CH2-Y unit. The doublets at
198 is in the carbonyl region, most likely an aldehyde or ketone. Two of the three CH2 groups are shifted by electronegative groups, suggesting a X-CH2-CH2-CH2-Y unit. The doublets at  129 and 145 are in the alkene region, suggesting a -CH
129 and 145 are in the alkene region, suggesting a -CH CH- group. The three degrees of unsaturation suggests that the molecule also has a ring.
CH- group. The three degrees of unsaturation suggests that the molecule also has a ring.
这是什么,你为什么担心,刷了简单的事情,你会出来的天才,学我,小水珠做出的海洋,你将在这方面的专家

당신이 걱정하는 이유는 간단한 것들로 브러시, 무엇인가, 당신은 천재 나올 나와 함께 배울 것, 물 작은 방울은 바다를 만들어,이 분야의 전문가가 될 것입니다
- Electronegative groups are "deshielding" and tend to move NMR signals from attached carbons further "downfield" (to higher ppm values).
- The
-system of alkenes, aromatic compounds and carbonyls strongly deshield
C nuclei and move them "downfield" to higher ppm values.
- Carbonyl carbons are strongly deshielded and occur at very high ppm values. Within this group, carboxylic acids and esters tend to have the smaller
values, while ketones and aldehydes have values
200.
The 13C chemical shift is dependent both on the presence of electronegative groups and on the steric environment. This is best demonstrated by examining a variety of hexane isomers:
 25 - 45. Methyl groups which terminate unbranched alkyl chains, however, are significantly shielded (moved to lower
25 - 45. Methyl groups which terminate unbranched alkyl chains, however, are significantly shielded (moved to lower  values), as shown by the examples above (
values), as shown by the examples above ( 14, 14.3 and 8.7). The origin of this effect is thought to be steric compression in the gamma (
14, 14.3 and 8.7). The origin of this effect is thought to be steric compression in the gamma ( ) position due to gauche interactions. This is shown schematically below and the gamma position is marked above in the example for hexane.
) position due to gauche interactions. This is shown schematically below and the gamma position is marked above in the example for hexane. 65 - 90, as shown in the examples below:
65 - 90, as shown in the examples below: 30 - 50 region, as shown below. The effects are not simply additive, however, and multiple substitution can often be shielding (move the signal to lower
30 - 50 region, as shown below. The effects are not simply additive, however, and multiple substitution can often be shielding (move the signal to lower  values). The nitrile carbon is significantly shielding and adjacent carbons tend to occur in the
values). The nitrile carbon is significantly shielding and adjacent carbons tend to occur in the  20 - 25 region.
20 - 25 region. 110 - 140, as shown in the examples below. Conjugation between alkene centers has little effect, as demonstrated by the two middle structures shown below. Conjugation with an oxygen, however, has a dramatic shielding effect, which is attributed to contributions from the resonance forms shown below.
110 - 140, as shown in the examples below. Conjugation between alkene centers has little effect, as demonstrated by the two middle structures shown below. Conjugation with an oxygen, however, has a dramatic shielding effect, which is attributed to contributions from the resonance forms shown below. 65 -85, and are significantly shielding to the carbons which are immediately adjacent (
65 -85, and are significantly shielding to the carbons which are immediately adjacent ( 1.5 for the terminal methyl of 2-pentyne).
1.5 for the terminal methyl of 2-pentyne). 170 - 210 with esters, carboxylic acids and amides at the low end, and simple ketones and aldehydes at the high end of the range.
170 - 210 with esters, carboxylic acids and amides at the low end, and simple ketones and aldehydes at the high end of the range. 120 - 140 and are shifted within this range by the nature of the attached substituent. The multiplicity of aromatic peaks in the non-decoupled spectrum is useful for identifying aromatic substitution patterns.
120 - 140 and are shifted within this range by the nature of the attached substituent. The multiplicity of aromatic peaks in the non-decoupled spectrum is useful for identifying aromatic substitution patterns.
آپ پریشان کیوں ہیں اس سادہ چیزوں کے ساتھ برش،، کیا ہے، آپ، ہوشیار باہر آ میرے ساتھ سیکھ جائے گی، پانی کے چھوٹے چھوٹے قطرے ایک سمندر بنانے کے لئے، آپ کو اس میں ایک ماہر ہو جائے گا
| Shift (ppm) | |
| 145.2 | 128.0 |
| 132.2 | 56..5 |
| 130.2 | 21.4 |

DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO Ph.D
amcrasto@gmail.com
MOBILE-+91 9323115463
GLENMARK SCIENTIST , INDIA
web link
web link
http://anthonycrasto.jimdo.com/
blogs are



Congratulations! Your presentation titled "Anthony Crasto Glenmark scientist, helping millions with websites" has just crossed MILLION views.
アンソニー 安东尼 Энтони 안토니 أنتوني
join my process development group on google
you can post articles and will be administered by me on the google group which is very popular across the world
LinkedIn group
blogs are

MY BLOG ON MED CHEM
New Drug Approvals
ALL ABOUT DRUGS
WORLD DRUG TRACKER
MEDICINAL CHEM INTERNATIONAL
DRUG SYN INTERNATIONAL
SCALEUP OF DRUGS
ALL FOR DRUGS ON WEB
http://scholar.google.co.uk/citations?user=bxm3kYkAAAAJ
VIETNAM
http://me.zing.vn/u/amcrasto
ICELAND
http://amcrasto.bland.is/
RUSSIA
http://www.100zakladok.ru/amcrasto/
http://bobrdobr.ru/people/amcrasto/
New Drug Approvals
ALL ABOUT DRUGS
WORLD DRUG TRACKER
MEDICINAL CHEM INTERNATIONAL
DRUG SYN INTERNATIONAL
SCALEUP OF DRUGS
ALL FOR DRUGS ON WEB
http://scholar.google.co.uk/citations?user=bxm3kYkAAAAJ
MY CHINA AND JAPAN BLOGS
http://me.zing.vn/u/amcrasto
ICELAND
http://amcrasto.bland.is/
RUSSIA
http://www.100zakladok.ru/amcrasto/
http://bobrdobr.ru/people/amcrasto/

Location of Khajuraho Group of Monuments in India.

Hotel Chandela - A Taj Leisure Hotel
|


 -system of alkenes, aromatic compounds and carbonyls strongly deshield
-system of alkenes, aromatic compounds and carbonyls strongly deshield 
 C nuclei and move them "downfield" to higher ppm values.
C nuclei and move them "downfield" to higher ppm values.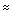 200.
200.
I am grateful for this blog to distribute knowledge about this significant topic. Here I found different segments and now I am going to use these new instructions with new enthusiasm.bioresonantie friesland
ReplyDelete