STRUCTURE 4
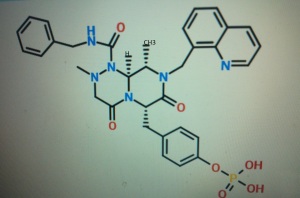
4-(((6S,9S,9aS)-l-(benzylcarbamoyl)-2,9-dimethyl-4,7-dioxo-8-(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)octahydro- 1 H-pyrazino[2, 1 -c] [ 1 ,2,4]triazin-6-yl)methyl)phenyl dihydrogen phosphate
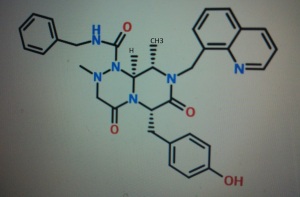

STRUCTURE 5
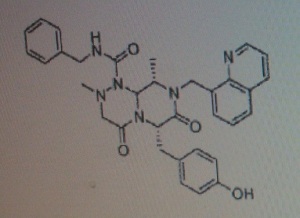
(6S,9S,9aS)-N-benzyl-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-2,9-dimethyl-4,7-dioxo-8-(quinolin-8-yImethyl)octahydro- 1 H-pyrazino[2, 1 -c] [ 1 ,2,4]triazine- 1 -carboxamide.
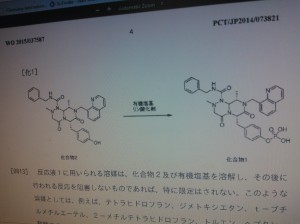
compd 2 and 1
OR
compd 3.above both str are same(6S,9aS)-N-Benzyl-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-8-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)-4,7-dioxoperhydropyrazino[1,2-a]pyrimidine-1-carboxamide
One of compd 1,2, 3, 4, 5 see at the end as update IS ICG001, PRI-724,
ICG001, also known as PRI-724, is a potent, specific inhibitor of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway in cancer stem cells with potential antineoplastic activity. Wnt signaling pathway inhibitor PRI-724 specifically inhibits the recruiting of beta-catenin with its coactivator CBP (the binding protein of the cAMP response element-binding protein CREB); together with other transcription factors beta-catenin/CBP binds to WRE (Wnt-responsive element) and activates transcription of a wide range of target genes of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Blocking the interaction of CBP and beta-catenin by this agent prevents gene expression of many proteins necessary for growth, thereby potentially suppressing cancer cell growth. The Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway regulates cell morphology, motility, and proliferation; aberrant regulation of this pathway leads to neoplastic proliferation.
 JAPAN
JAPAN
4-(((6S,9S)-l-(benzylcarbamoyl)-2,9-dimethyl-4,7-dioxo-8-(quinoline-8-ylmethyl) octahy- dro-1H-pyrazino[2,1-c][1,2,4]triazine-6-yl)methyl) phenyl dihydrogen phosphate
(6S,9S)-N-benzyl-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-2,9-dimethyl-4,7-dioxo-8-(quinoline-8-ylmethyl) octahydro-1H-pyrazino[2,1-c] [I,z,4]triazine-1-carboxamide,
Compound A as in wo 2014061827........4-(((6S,9S,9aS)-l-(benzylcarbamoyl)-2,9-dimethyl-4,7-dioxo-8-(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)octahydro- 1 H-pyrazino[2, 1 -c] [ 1 ,2,4]triazin-6-yl)methyl)phenyI dihydrogen phosphate in WO2014061827
4-(((6S,9S,9aS)-l-(benzylcarbamoyl)-2,9-dimethyl-4,7-dioxo-8-(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)octahydro- 1 H-pyrazino[2, 1 -c] [ 1 ,2,4]triazin-6-yl)methyl)phenyl dihydrogen phosphate
(6S,9S,9aS)-N-benzyl-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-2,9-dimethyl-4,7-dioxo-8-(quinolin-8-yImethyl)octahydro- 1 H-pyrazino[2, 1 -c] [ 1 ,2,4]triazine- 1 -carboxamide.
4-(((6S,9S)-1-(benzylcarbamoyl)-2,9-dimethyl-4,7-dioxo-8-(quinoline-8-ylmethyl)octahydro-1H-pyrazino[2,1-c][1,2,4]triazine-6-yl)methyl)phenyl dihydrogen phosphate (presumed to be PRI-724; first disclosed in WO2009148192), useful for treating cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, glaucoma and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Eisai, under license from PRISM Pharma, is developing PRI-724, an inhibitor of CREB binding protein or beta-catenin complex formation, for treating cancer (phase 1, as of March 2015) and HCV-induced cirrhosis (preclinical trial).
Follows on from WO2014061827, claiming the use of PRI-724 for treating pulmonary fibrosis.
IS IT

cas 847591-62-2............http://www.medkoo.com/Anticancer-trials/PRI-724.htm
(6S,9aS)-N-Benzyl-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-8-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)-4,7-dioxoperhydropyrazino[1,2-a]pyrimidine-1-carboxamide
(6S,9aS)-N-Benzyl-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-8-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)-4,7-dioxoperhydropyrazino[1,2-a]pyrimidine-1-carboxamide
COMPD 3
OR
COMPD 2
PRI724
1198780-43-6, 578.66, C33 H34 N6 O4
(6S,9S)-N-benzyl-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-2,9-dimethyl-4,7-dioxo-8-(quinoline-8-ylmethyl) octahydro-1H-pyrazino[2,1-c] [I,z,4]triazine-1-carboxamide,
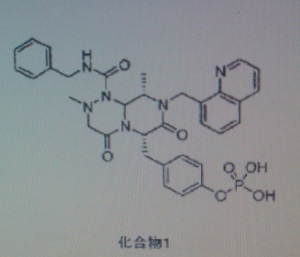

COMPD1
PRI 724
4-(((6S,9S)-l-(benzylcarbamoyl)-2,9-dimethyl-4,7-dioxo-8-(quinoline-8-ylmethyl) octahy- dro-1H-pyrazino[2,1-c][1,2,4]triazine-6-yl)methyl) phenyl dihydrogen phosphate
COMPD 1
SEE

SEE
Eisai Research Institute; PRISM Pharma Co Ltd
出願人:エ_ ザイ■ ア_ ル■ アンド■ ディ_ ■
マネジメン卜株式会社(EISAI R&D MANAGEMENT
CO., LTD.) [JP /JP ];亍1128088 東京都文京区
小石川四丁目6 番1 O 号Tokyo (JP).株式会社P
R I S M P h a r m a (PRISM PHARMA CO.,
LTD.) [JP /JP ];亍2268510神奈川県横浜市緑区長津
田町 4 2 5 9 — 3 Kanagawa (JP)
マネジメン卜株式会社(EISAI R&D MANAGEMENT
CO., LTD.) [JP /JP ];亍1128088 東京都文京区
小石川四丁目6 番1 O 号Tokyo (JP).株式会社P
R I S M P h a r m a (PRISM PHARMA CO.,
LTD.) [JP /JP ];亍2268510神奈川県横浜市緑区長津
田町 4 2 5 9 — 3 Kanagawa (JP)
(IO) 国際公開番号
2 0 1 5 ^ ® S 3 .2 0 1 5 )
2 0 1 5 ^ ® S 3 .2 0 1 5 )
WO 2015/037587 Al
This method of producing 4-(((6S,9S)-l-(benzylcarbamoyl)-2,9-dimethyl-4,7-dioxo-8-(quinoline-8-ylmethyl) octahy- dro-1H-pyrazino[2,1-c][1,2,4]triazine-6-yl)methyl) phenyl dihydrogen phosphate involves a step for adding a reaction solution (I) comprising (6S,9S)-N-benzyl-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-2,9-dimethyl-4,7-dioxo-8-(quinoline-8-ylmethyl) octahydro-1H-pyrazino[2,1-c] [I,z,4]triazine-1-carboxamide, triethylamine and a solvent to a reaction solution (2) comprising a phosphorylating agent and a solvent.
1
1H-NMR (600MHz, METHAN0L-d4) δ (ppm):1.15 (d, J=6 Hz, 3H), 2.65 (s, 3H), 3.12 (d, J=18 Hz, 1H), 3.35 (d, J=7 Hz, 2H), 3.48 (d, J=18 Hz,1H), 4.15 (m,1H), 4.32 (d, J=15 Hz, 1H), 4.40 (d, J=15 Hz, 1H), 5.33(d, J=16 Hz, 1H), 5.41(d, J=16 Hz, 1H), 5.44 (d, J=7 Hz, 1H), 5.64 (d, J=10 Hz, 1H), 7.07 (dd, J=9,1 Hz, 2H), 7.15 (d, J=9 Hz, 2H), 7.24 (t, J=7 Hz, 1H), 7.27 (d, J=7 Hz, 2H), 7.34 (t, J=8 Hz, 2H), 7.55 (d d, J=8, 4 Hz, 1H), 7.60 (brd, J=6 Hz, 1H), 7.62 (dd, J=8, 7 Hz, 1H), 7.88 (dd, J=8,1 Hz, 1H), 8.38 (dd, J=8, 2 Hz, 1H), 8.90 (dd, J =4, 2 Hz, 1H).
...............................................................................
SEE
SYNTHESIS OF COMPD 2
PART A
Synthesis Part A
step A
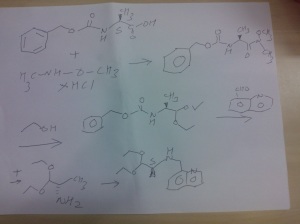
(S)-benzyl 1-(methoxy(methyl)amino)-1-oxopropan-2-ylcarbamate
Reaction of the foll...................N-methoxy-N-methylamine hydrochloride, 1N sodium hydroxide , (S)-2-(benzyloxycarbonylamino)propanoic acidand 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methylmorpholinium chloride to obtain
(S)-benzyl 1-(methoxy(methyl)amino)-1-oxopropan-2-ylcarbamate.
STEP B
(S)-benzyl 1,1-diethoxypropan-2-ylcarbamate
Reaction of the foll...................(S)-benzyl 1-(methoxy(methyl)amino)-1-oxopropan-2-ylcarbamate, 2M lithium aluminium hydride in tetrahydrofuran solution to obtain (S)-benzyl 1,1-diethoxypropan-2-ylcarbamate
STEP C
(S)-1,1-diethoxypropan-2-amine
Reaction of the foll...................(S)-benzyl 1,1-diethoxypropan-2-ylcarbamate, 5% palladium on carbon title compound . (S)-1,1-diethoxypropan-2-amine,
STEP D
(S)-1,1-diethoxy-N-(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)propan-2-amine,
Reaction of the foll...................(S)-1,1-diethoxypropan-2-amine,was reacted with 8-Quinolinecarboaldehyde to obtain the title
compound (S)-1,1-diethoxy-N-(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)propan-2-amine
PART B
STEP E
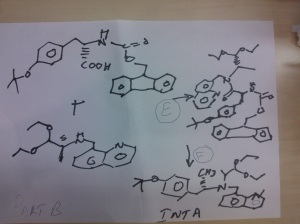
(9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (S)-3-(4-tert-butoxyphenyl)-1-(((S)-1,1-diethoxypropan-2-yl)(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)amino)-1-oxopropan-2-ylcarbamate
Reaction of the foll................... (S)-1,1-diethoxy-N-(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)propan-2-amine, (S)-2-(((9H-fluoren-9-yl)methoxy)carbonylamino)-3-(4-tertbutoxyphenyl)propanoic acid to obtain the title compound (9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (S)-3-(4-tert-butoxyphenyl)-1-(((S)-1,1-diethoxypropan-2-yl)(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)amino)-1-oxopropan-2-ylcarbamate
STEP f
(S)-2-amino-3-(4-tertbutoxyphenyl)-N-((S)-1,1-diethoxypropan-2-yl)-N-(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)propanamide INT A
Reaction of the foll................... (9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (S)-3-(4-tert-butoxyphenyl)-1-(((S)-1,1-diethoxypropan-2-yl)(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)amino)-1-oxopropan-2-ylcarbamate and piperidine to
obtain the title compound (S)-2-amino-3-(4-tertbutoxyphenyl)-N-((S)-1,1-diethoxypropan-2-yl)-N-(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)propanamide INT A
obtain the title compound (S)-2-amino-3-(4-tertbutoxyphenyl)-N-((S)-1,1-diethoxypropan-2-yl)-N-(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)propanamide INT A
PART C
STEP g
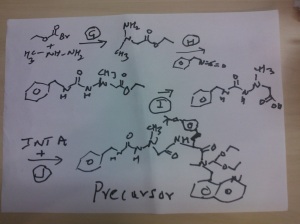
ethyl 2-(1-methylhydrazinyl)acetate
Reaction of the foll...................methylhydrazine 7 was reacted with ethyl 2-bromoacetate 1to obtain the title compound
STEP h
ethyl 2-(1-Methyl-2-(benzylcarbamoyl)hydrazinyl)acetate
ethyl 2-(1-Methyl-2-(benzylcarbamoyl)hydrazinyl)acetate
Reaction of the foll................... ethyl 2-(1-methylhydrazinyl)acetateand benzyl isocyanate to obtain the title
compound ethyl 2-(1-Methyl-2-(benzylcarbamoyl)hydrazinyl)acetate
compound ethyl 2-(1-Methyl-2-(benzylcarbamoyl)hydrazinyl)acetate
STEP i
2-(2-(benzylcarbamoyl)-1-methylhydrazinyl)acetic acid
2-(2-(benzylcarbamoyl)-1-methylhydrazinyl)acetic acid
Reaction of the foll................... ethyl 2-(1-allyl-2-
(benzylcarbamoyl)hydrazinyl)acetate and lithium hydroxide monohydrate to obtain the title compound 2-(2-(benzylcarbamoyl)-1-methylhydrazinyl)acetic acid
(benzylcarbamoyl)hydrazinyl)acetate and lithium hydroxide monohydrate to obtain the title compound 2-(2-(benzylcarbamoyl)-1-methylhydrazinyl)acetic acid
STEP j
N-benzyl-2-(2-((S)-3-(4-tert-butoxyphenyl)-1-(((S)-1,1-
diethoxypropan-2-yl)(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)amino)-1-oxopropan-2-ylamino)-2-oxoethyl)-2-
methylhydrazinecarboxamide......... precursor
N-benzyl-2-(2-((S)-3-(4-tert-butoxyphenyl)-1-(((S)-1,1-
diethoxypropan-2-yl)(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)amino)-1-oxopropan-2-ylamino)-2-oxoethyl)-2-
methylhydrazinecarboxamide......... precursor
Reaction of the foll................... 2-(2-(benzylcarbamoyl)-1-methylhydrazinyl)acetic acid and (S)-2-amino-3-(4-tert-butoxyphenyl)-N-((S)-1,1-diethoxypropan-2-yl)-N-(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)propanamide ( INT A )yielded the title compound ie the precursor
PART D
THIS PRECURSOR GIVES FINAL PRODUCT
Synthesis of (6S,9S)-N-benzyl-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-2,9-
dimethyl-8-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)-4,7-dioxooctahydro-1H-pyrazino[2,1-c][1,2,4]triazine-1-
carboxamide ..........final
dimethyl-8-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)-4,7-dioxooctahydro-1H-pyrazino[2,1-c][1,2,4]triazine-1-
carboxamide ..........final
fOLL reactants........... N-benzyl-2-(2-((S)-3-(4-tert-butoxyphenyl)-1-(((S)-1,1-diethoxypropan-2-yl)(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)amino)-1-oxopropan-2-ylamino)-2-oxoethyl)-2-methylhydrazinecarboxamide, ie the precursor and 10%-water/HCOOH gave (6S,9S)-N-benzyl-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-2,9-dimethyl-4,7-dioxo-8-(quinolin-8-ylmethyl)octahydro-1Hpyrazino[2,1-c][1,2,4]triazine-1-carboxamide
RT 4.22; Mass 578.9
COMPD 3

(6S,9aS)-N-Benzyl-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-8-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)-4,7-dioxoperhydropyrazino[1,2-a]pyrimidine-1-carboxamide
SEE
US 6762185
...................................
SEE

novel compounds, agent for inducing differentiation into hepatocytes of mesenchymal stem cells, Wnt / β- catenin signaling pathway inhibitor, method for producing hepatocytes with them on hepatocytes such as by their production.
Liver disease is said to be Japan's national disease, a large number of patients suffering from liver disease. In addition, the annual number of deaths from hepatocellular carcinoma amounts to about 30 004 thousand people. Recently, hepatocellular cancer outcome is improved by advances in treatment, but the increase of advanced cancer, with hepatic dysfunction cirrhosis to merge, so-called hepatic failure death has increased. Liver failure therapy, although liver transplantation is ideal, it is difficult in Japan to obtain sufficient donors, it is necessary to develop a liver regeneration therapy with stem cells.
As stem cells that have the potential to differentiate into liver cells, bone marrow cells, tissue stem cells, such as umbilical cord blood cells can be expected.Therefore, a number of research institutions, for the realization of by regenerative medicine liver cell transplantation treatment of chronic liver failure patient, to differentiate human tissue stem cells into functional hepatocytes, truly clinically applicable efficient differentiation induction technology you are conducting research and development with the goal of developing a.
For example, in the laboratory of Shioda Professor of Tottori University Graduate School of Medicine, reported that the Wnt / β- catenin signaling pathway were differentiated into hepatocytes showed that suppressed by RNA interference at the time of induction of differentiation from human mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes you are (Non-Patent Document 1 and Non-Patent Documents 3-5).Furthermore, studies to induce differentiation of hepatocytes in other institutions have been conducted (Non-Patent Document 2, Patent Documents 1 and 2).
On the other hand, recently, from 4,000 or more screening of large compound libraries, Wnt / β- catenin signaling pathway inhibitory low molecular compound 5 types have been identified (Non-Patent Documents 6-9).
Kohyo 2009-535035 JP Patent Publication No. 2010-75631
Atsushi Yanagitani et al., " retinoic Acid Receptor Dominant Level Negative Form Causes steatohepatitis and Liver Tumors in Transgenic Mice ", Hepatology, Vol. 40, No. 2, 2004, P. 366-375 Seoyoung Park et al.,"Hexachlorophene Inhibits Wnt / beta-catenin Pathway by Promoting Siah-Mediated beta-catenin Degradation ", Mol Pharmacol Vol. 70, No. 3, 960-966, 2006 Yoko Yoshida et al.," A role of Wnt / beta-catenin Signals in hepatic fate Specification of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells ", Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 293:. G1089-G1098, 2007 Shimomura T et al," Hepatic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived UE7T-13 cells: Effects of cytokines and CCN family Gene expression ", Hepatol Res., 37, 1068-79, 2007 Ishii K et al.," Hepatic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by tetracycline-regulated Hepatocyte Nuclear factor 3Beta "Hepatology, 48, 597- 606, 2008 Maina Lepourcelet et al., " Small-molecule Antagonists of the oncogenic Tcf / beta-catenin protein complex ", CANCER CELL, JANUARY 2004, VOL. 5, 91-102 Emami KH et al.," A Small molecule inhibitor of beta-catenin / CREB-binding protein Transcription ", Proc Natl Acad Sci US A. 2004 Aug 24; 101 (34):.. 12682-7 Jufang Shan et al,"Identification of a Specific Inhibitor of the Dishevelled PDZ Domain " , Biochemistry 2005 Nov 29; 44 (47):.. 15495-503 Trosset JY et al, " Inhibition of protein-protein Interactions: the discovery of beta-catenin Druglike Inhibitors by combining virtual and Biophysical Screening . ", Proteins 2006 Jul 1 ; 64 (1): 60-7
However, the conventional techniques described above literature, had a room for improvement in the following points.
Patent Documents 1 and 2, it has been described for proteins to induce stem cells from Hikimomiki cells, due to the use of the protein formulation as a differentiation inducing agent, a room for further improvement in terms of stability and safety and there was.
Patent Documents 1 and 2, it has been described for proteins to induce stem cells from Hikimomiki cells, due to the use of the protein formulation as a differentiation inducing agent, a room for further improvement in terms of stability and safety and there was.
Non-Patent Document 1 and Non-Patent Document 3 to 5, and have reported that induced differentiated hepatocytes from human mesenchymal stem cells, the use of siRNA as a differentiation inducing agent, such as stability and safety there is room for further improvement in the surface. Non-Patent Document 2, 6 to 9, is not described with respect to method of inducing differentiation into hepatocytes.
The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object thereof is to provide an effective low-molecular compounds that induce differentiation into hepatocytes from mesenchymal stem cells. Or, it is intended that the low-molecular compound was used to provide a secure differentiation inducing method is excellent from the mesenchymal stem cell differentiation efficiency of liver cells.
According to the present invention, there is provided formula (1) and one or more compounds selected from the group of compounds represented by the formula (2), a salt thereof or a solvate thereof.
<Example 1> synthetic ICG-001 of synthesis (1) ICG-001 of the IC-2 is an oligopeptide having two rings of β- turn mimic structure in central skeleton, and transcription by β-catenin / Tcf complex can function as a potent antagonist for activation has been reported (Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 1467-1474). Synthesis of ICG-001 in accordance with the literature (Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 12912-12916), was subjected to examination.
(1-1) of Compound 1 Synthesis 1-naphtaldehyde (Wako Pure Chemical) (1.56 g, 10 mmol) and 2,2-diethoxyethanamine (Tokyo Kasei Kogyo) (1.33 g, 10 mmol) were mixed 100 I was stirred 20 min at o C. After cooling to room temperature, diluted with EtOH (20 mL), was added portionwise NaBH 4 (0.38 g, 10 mmol), at room temperature, and stirred for 16 h. After completion of the reaction, was distilled off by concentration under reduced pressure EtOH, the product was extracted with AcOEt. The resulting product was purified by silica gel column chromatography (hexane / AcOEt = 5/1) to give the to give compound 1 (2.29 g, 8.5 mmol, 85%).
(1-2) Synthesis of Compound 3 Fmoc-L-Tyr (t-Bu) -OH (0.87 g, 1.9 mmol) in DMF (7 mL) solution of a condensing agent HATU (0.76 g, 2.0 mmol) and diisopropylethylamine (DIEA) (0.35 mL, 2.0 mmol) was added and after stirring for 20 min, compound 1 (0.54 g, a 2.0 mmol) was added, at room temperature, 16 h the mixture was stirred. After the reaction, DMF was distilled off by concentration under reduced pressure, and the resulting product was purified by column chromatography (hexane / AcOEt = 10/1), compound 2 was obtained (1.33 g, 1.9 mmol, 93%). The resulting compound 2 (1.33 g, 1.9 mmol) was dissolved in CH 2 Cl 2 (20 mL), was added diethylamine (DEA) (10 ml, excess), at room temperature, was 2 h stirring.After confirming the completion of the reaction by TLC, vacuum was distilled off CH 2 Cl 2 by concentration, the resulting product was purified by silica gel column chromatography (AcOEt), to give compound 3 (0.92 g, 1. 8 mmol, 92%).
(1-3) Synthesis Fmoc-β-Ala-OH (0.53 g, 1.7 mmol) of compound 5 in DMF (8 mL) solution of a condensing agent HATU (0.70 g, 1.8 mmol) and diisopropylethylamine (DIEA) (0.32 mL, 1.8 mmol) was added and after stirring for 20 min, compound 3 (0.92 g, 1.8 mmol) was added, at room temperature, and stirred for 14 h. After the reaction, DMF was distilled off by concentration under reduced pressure, the resulting product was purified by column chromatography (hexane / AcOEt = 1/1), compound 4 was obtained (1.2 g, 1.5 mmol, 82%). Obtained compound 4 (1.2 g, 1.5 mmol) was dissolved in CH 2 Cl 2 (20 mL), was added diethylamine (DEA) (9 mL, excess), at room temperature, and stirred for 1 h. After confirming the completion of the reaction by TLC, was distilled off CH 2 Cl 2 by concentration under reduced pressure, and the resulting product was purified by silica gel column chromatography (AcOEt / EtOH = 1/1), to give compound 5 (0 .66 g, 1.2 mmol, 80%).
(1-4) synthetic compounds 5 (0.66 g, 1.2 mmol) of compound 7 CH 2 Cl 2 of solution (8 mL) to benzylisocyanate (0.16 g, 1.2 mmol) of CH 2 Cl 2 solution (8 mL) was added, at room temperature, and stirred for 12 h. After confirming the completion of the reaction by TLC, was distilled off CH 2 Cl 2 by concentration under reduced pressure, and the resulting product was purified by column chromatography (AcOEt / EtOH = 1/1), to give compound 6 (0. 59 g, 0.85 mmol, 73%). The obtained compound 6 (0.59 g, 0.85 mmol) at room temperature in the formic acid (9 ml), I was stirred 20 h. Was evaporated formic acid by concentration under reduced pressure, the resulting product was purified by column chromatography (AcOEt), Compound 7a to (ICG-001) was obtained as a white solid (0.26 g, 0.48 mmol, 57 %).
The resulting product, MS spectra and were identified from the 1 H NMR spectrum (with the literature value) (Fig. 1).
The resulting product, MS spectra and were identified from the 1 H NMR spectrum (with the literature value) (Fig. 1).
 COCK SAYS MOM CAN TEACH YOU NMR
COCK SAYS MOM CAN TEACH YOU NMR
 DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO .....FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO .....FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
 amcrasto@gmail.com
amcrasto@gmail.com


















.png)

.png)






.png)
