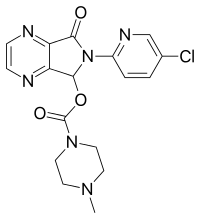
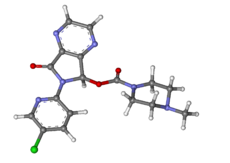
VALSARTAN
mp 114–118 °C;
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 12.6 (brs, 1H), 7.72 (m, 4H), 7.24 (m, 1H), 7.15 (m, 2H), 6.94 (m, 1H), 4.58 (m, 1H), 4.40 (m, 1H), 3.33 (m, 1H), 2.25 (m, 1H), 1.52 (m, 6H), 0.9 (m, 3H), 0.84 (m, 3H), 0.74 (m, 3H);
13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 174.0, 172.4, 171.8, 141.7, 138.2, 131.54, 131.1, 131.0, 129.3,128.8, 128.2, 127.4, 126.7, 70.3, 63.4, 49.9, 32.9, 28.05, 27.3, 22.2, 20.6, 14.2;
ESIMS: m/z calcd [M]+: 435; found: 436 [M+H]+; HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd [M]+: 435.5187; found: 435.5125 [M]+
US 7439261 B2
1H-NMR (CDCl3) (0.80-1.15 (m, 9H); 1.20-1.50 (m, 2H); 1.60-1.80 (m, 2H); 2.60 (t, 2H); 2.65-2.80 (m, 2H), 3.70 (d, 1H), 4.10 (d, 0.3 H), 4.30 (d, 0.7 H), 4.90 (d, 0.7H), 5.2 (d, 0.3H); 7.00 (d, 0.3H); 7.10-7.20 (m, 4H), 7.40-7.60 (m, 3H), 7.85 (d, 0.7 H).
SHORT DESCRIPTION
Valsartan, N-(1-oxopentyl)-N-[[2′-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-L-valine, is a known anti-hypertensive agent having the following formula (I):
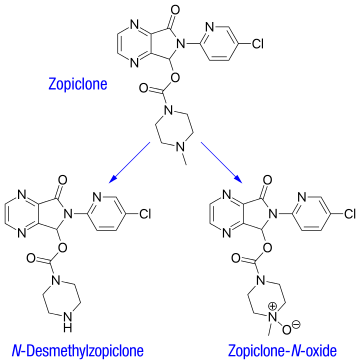
Valsartan and its preparation are disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 5,399,578, in particular in Example 16. One of the synthetic routes according to U.S. Pat. No. 5,399,578 can be schematically represented as follows:
The synthetic pathway comprises various steps, among which:
- coupling of compound (3) with 2-chlorobenzonitrile to obtain compound (4),
- radicalic bromination of compound (4) to give compound (5),
- transformation of the brominated derivative (5) into the respective aldehyde derivative (6),
- reductive alkylation of compound (6) to obtain intermediate (8),
- acylation of compound (8) to obtain intermediate (9),
- conversion of the cyano group to the tetrazole group to afford intermediate (10),
- deprotection of the carboxylic group by hydrogenolysis to obtain valsartan.
- It is marketed as the free acid under the name DIOVAN. DIOVAN is prescribed as oral tablets in dosages of 40 mg, 80 mg, 160 mg and 320 mg ofvalsartan.
- [0004]Valsartan and/or its intermediates are disclosed in various references, including:
U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,399,578 ,5,965,592 ,5,260,325 ,6,271,375 ,WO 02/006253 WO 01/082858 WO 99/67231 WO 97/30036 - [0005]Valsartan is an orally active specific angiotensin II antagonist acting on the AT1 receptor subtype. Valsartan is prescribed for the treatment of hypertension.
U.S. Pat. No. 6,395,728 is directed to use of valsartan for treatment of diabetes related hypertension.U.S. Pat. Nos. 6,465,502 and6,485,745 are directed to treatment of lung cancer with valsartan.U.S. Pat. No. 6,294,197 is directed to solid oral dosage forms of valsartan
http://users.uoa.gr/~tmavrom/2009/valsartan2009.pdf
http://www.acgpubs.org/JCM/2009/Volume%203/Issue%201/JCM-0908-14.pdf
https://www.beilstein-journals.org/bjoc/single/printArticle.htm?publicId=1860-5397-6-27 REPORTS
mp 114–118 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 12.6 (brs, 1H), 7.72 (m, 4H), 7.24 (m, 1H), 7.15 (m, 2H), 6.94 (m, 1H), 4.58 (m, 1H), 4.40 (m, 1H), 3.33 (m, 1H), 2.25 (m, 1H), 1.52 (m, 6H), 0.9 (m, 3H), 0.84 (m, 3H), 0.74 (m, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 174.0, 172.4, 171.8, 141.7, 138.2, 131.54, 131.1, 131.0, 129.3,128.8, 128.2, 127.4, 126.7, 70.3, 63.4, 49.9, 32.9, 28.05, 27.3, 22.2, 20.6, 14.2; ESIMS: m/z calcd [M]+: 435; found: 436 [M+H]+; HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd [M]+: 435.5187; found: 435.5125 [M]+
Valsartan
Structural formula
UV - Spectrum
IR - spectrum
NMR spectrum
references
- UV and IR Spectra. H.-W. Dibbern, R.M. Muller, E. Wirbitzki, 2002 ECV
- NIST/EPA/NIH Mass Spectral Library 2008
- Handbook of Organic Compounds. NIR, IR, Raman, and UV-Vis Spectra Featuring Polymers and Surfactants, Jr., Jerry Workman. Academic Press, 2000.
- Handbook of ultraviolet and visible absorption spectra of organic compounds, K. Hirayama. Plenum Press Data Division, 1967.

CLIP
Scheme 2: (a) Et3N, CH2Cl2, 0 °C, 95%; (b) NaH, THF, 70%; (c) n-BuLi, 25 °C, THF, anhyd ZnCl2, −20 °C, Q-phos, Pd(OAc)2, 75 °C, 2 h, 80%; (d) 3 N NaOH, MeOH, reflux, 90%.
http://www.beilstein-journals.org/bjoc/single/articleFullText.htm?publicId=1860-5397-6-27
valsartan 8; mp 114–118 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 12.6 (brs, 1H), 7.72 (m, 4H), 7.24 (m, 1H), 7.15 (m, 2H), 6.94 (m, 1H), 4.58 (m, 1H), 4.40 (m, 1H), 3.33 (m, 1H), 2.25 (m, 1H), 1.52 (m, 6H), 0.9 (m, 3H), 0.84 (m, 3H), 0.74 (m, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 174.0, 172.4, 171.8, 141.7, 138.2, 131.54, 131.1, 131.0, 129.3,128.8, 128.2, 127.4, 126.7, 70.3, 63.4, 49.9, 32.9, 28.05, 27.3, 22.2, 20.6, 14.2; ESIMS: m/z calcd [M]+: 435; found: 436 [M+H]+; HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd [M]+: 435.5187; found: 435.5125 [M]+
/////////