
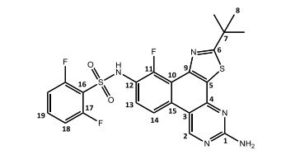
N-(5-amino-2-tert-butyl)-11-fluorbenzol[f]thiazol-[4,5-h]-quinazolin-10-yl)-2,6-difluorbenzolsulfonamide = Dabrafenib_photo (2)
C23H18F3N5O2S2 (Mr = 517.09)
Solution of 5 mg (9.6 μmol) dabrafenib in 2 ml THF was irradiated at 365 nm with 5.4 W for 2 min. This procedure was repeated 18 times at room temperature. The reaction batches were combined. The total initial weight of dabrafenib was 101 mg (190 μmol). The solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was purified by the flash chromatography (SiO2 reversed phase, MeOH/water gradient 50:50 to 100:0) to give compound 2 as a yellowish solid (36.2 mg, 70.0 μmol, yield: 37%).
1H-NMR (DMSO-d6 , 300 MHz): δ = 1.52 (s, 9 H, H-8), 7.28 (m, 2 H, NH2), 7.28 (ddd, 5 J = 0.4 Hz, 4 J = 1.7 Hz, 3 J = 8.5 Hz, 3 J = 8.9 Hz, 2 H, H-18), 7.59 (dd, 3 J = 7.4 Hz, 3 J = 7.8 Hz, 1 H, H-13), 7.71 (tt, 4 J = 6.1 Hz, 3 J = 8.5 Hz, 1 H, H-19), 8.56 (dd, 4 J = 0.9 Hz, 3 J = 9.3 Hz, 1 H, H-14), 9.79 (s, 1 H, H-2), 11.01 (s, 1 H, NH) ppm.
13C-NMR (DMSO-d6 , 300 MHz): δ = 30.4 (s, C-8), 38.3 (s, C-7), 110.9 (d, 4 JCF = 1.6 Hz, C-3), 113.4 (dd, 2 JCF = 22.7 Hz, 2 JCH = 3.5 Hz, C-18), 114.6 (d, 3 JCF = 10.3 Hz, C-9), 117.4 (d, 2 JCF = 16.1 Hz, C-16), 117.6 (dd, 4 JCF = 0.54 Hz, 2 JCH = 4.4 Hz, C-13), 120.8 (d, 2 JCF = 12.3 Hz, C-10), 125.4 (s, C-13), 129.3 (d, 3 JCF = 3.9 Hz, C-15), 130.6 (s, C-5), 135.9 (tt, 3 JCF = 10.9 Hz, 2 JCH = 3.3 Hz, C-19), 148.8 (dd, 2 JCF = 0.54 Hz, 2 JCH = 7.2 Hz, C-12), 149.2 (s, C-4), 150.1 (s, C-11), 157.1 160.5 (dd, 3 JFF = 257.3 Hz, 2 JCF = 3.61 Hz, C-4), 157.9 (s, C-2), 162.1 (s, C-1), 184.0 (s, C-6) ppm.
15N-HMBC (DMSO-d6 , 300 MHz): δ = 9.79/-119.60, 11.01/-268.37 ppm. 19F-NMR (DMSO-d6 , 300 MHz): δ = -121.03 (s, 1 F, F-11), -107.18 (m, 2 F, F-17) ppm.
HRMS (EI, 205 °C, THF): m/z = 517.0849 [M]+ .
LC-MS (ESI, 70 eV, MeOH): tR = 9.3 min; m/z (%) = 518.1 (100) [M+H]+
IR (ATR): ̃ = 3490 (N-H), 3176 (arom. C-H), 2926 (C-H3), 1696 (N=N), 1613 (N-H), 1587, 1522, 1488, 1469 (arom. C=C), 1342 (sulfonamide), 1277, 1240, 1174 (C-F) cm-1 .
Photoinduced Conversion of Antimelanoma Agent Dabrafenib to a Novel Fluorescent BRAFV600E Inhibitor
Institute of Pharmacy, University of Kiel, Gutenbergstr. 76, D-24118 Kiel, Germany
ACS Med. Chem. Lett., Article ASAP
DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.6b00340
Publication Date (Web): September 20, 2016
Copyright © 2016 American Chemical Society
*E-mail: cpeifer@pharmazie.uni-kiel.de. Tel: +49-431-880-1137.
ACS Editors' Choice - This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes.
Abstract
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar) was approved in 2013 by the FDA as a selective single agent treatment for patients with BRAFV600E mutation-positive advanced melanoma. One year later, a combination of dabrafenib and trametinib was used for treatment of BRAFV600E/K mutant metastatic melanoma. In the present study, we report on hitherto not described photosensitivity of dabrafenib both in organic and aqueous media. The half-lives for dabrafenib degradation were determined. Moreover, we revealed photoinduced chemical conversion of dabrafenib to its planar fluorescent derivative dabrafenib_photo 2. This novel compound could be isolated and biologically characterized in vitro. Both enzymatic and cellular assays proved that 2 is still a potent BRAFV600E inhibitor. The intracellular formation of 2 from dabrafenib upon ultraviolet irradiation is shown. The herein presented findings should be taken in account when handling dabrafenib both in preclinical research and in clinical applications.
////////Photoinduced Conversion, Antimelanoma Agent, Dabrafenib, Novel Fluorescent BRAFV600E Inhibitor, BRAFV600E; Dabrafenib, fluorescent probe, kinase inhibitor, photoinduced conversion
Mutianyu
Great Wall of China at Mutianyu.










////////////
No comments:
Post a Comment