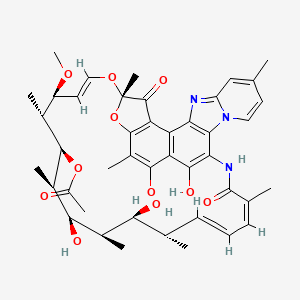
Rifaximin;
Rifaxidin; Rifacol; Xifaxan; Normix; Rifamycin L 105;L 105 (ansamacrolide antibiotic), L 105SV
(2S,16Z,18E,20S,21S,22R,23R,24R,25S,26S,27S,28E)-5,6,21,23,25-pentahydroxy-27-methoxy-2,4,11,16,20,22,24,26-octamethyl-2,7-(epoxypentadeca-[1,11,13]trienimino)benzofuro[4,5-e]pyrido[1,2-á]-benzimidazole-1,15(2H)-dione,25-acetate
CAS 80621-81-4, 4-Deoxy-4-methylpyrido[1,2-1,2]imidazo[5,4-c]rifamycin SV,
4-Deoxy-4′-methylpyrido[1′,2′-1,2]imidazo[5,4-c]rifamycin SV, Rifacol
| C43H51N3O11 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 785.87854 g/mol |
|---|
XIFAXAN tablets for oral administration are film-coated and contain 200 mg or 550 mg of rifaximin.
See synthesis
http://www.allfordrugs.com/2016/07/06/rifaximin/
SPECTRA
LINK IS CLICK
APT 13C NMR RIFAXIMIN
1H NMR PARTIAL
IR
Direct infusion mass analysis ESI (+)
IH NMR
- [-]ESI FRAG PATHWAY
PATENT
Patent US20130004576Rifaximin (INN; see The Merck Index, XIII Ed., 8304, CAS no. 80621-81-4), IUPAC nomenclature (2S,16Z,18E,20S,21S,22R,23R,24R,25S,26S,27S,28E)-5,6,21,23,25 pentahydroxy-27-methoxy-2,4,11,16,20,22,24,26-octamethyl-2,7-(epoxypentadeca-(1,11,13)trienimino)benzofuro(4,5-e)pyrido(1,2,-a)benzimidazole-1,15(2H)-dione,25-acetate) is a semi-synthetic antibiotic belonging to the rifamycin class of antibiotics. More precisely rifaximin is a pyrido-imidazo rifamycin described in the Italian patent IT 1154655, whereas the European patent EP 0161534 discloses a process for rifaximin production using rifamycin O as starting material (The Merck Index, XIII Ed., 8301).
U.S. Pat. No. 7,045,620, US 2008/0262220, US 7,612,199, US 2009/0130201 and Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2008, 10 1074-1081 (2008) disclose new forms of rifaximin.
WO 2008/035109 A1 discloses a process to prepare amorphous rifaximin, which comprises reaction of rifamycin S with 2-amino-4 picoline in presence of organic solvent like dichloromethane, ethylacetate, dichloroethylene, chloroform, in an inert atmosphere. When water is added to the reaction mixture, a solid precipitate corresponding to amorphous rifaximin is obtained.
The process described in this document can be assimilated to a crash precipitation, wherein the use of an anti-solvent causes the precipitation of rifaximin without giving any information about the chemical physical and biological characteristics of the rifaximin obtained.
WO 2009/108730 A2 describes different polymorphous forms of rifaximin and also amorphous forms of rifaximin. Amorphous forms are prepared by milling and crash precipitation and with these two different methods the amorphous rifaximin obtained from these two different processes has the same properties.
FIG. 4: 13C-NMR spectrum of rifaximin obtained by spray drying process.

FIG. 5: FT-IR spectrum of rifaximin obtained by spray drying process.

See synthesis
http://www.allfordrugs.com/2016/07/06/rifaximin/