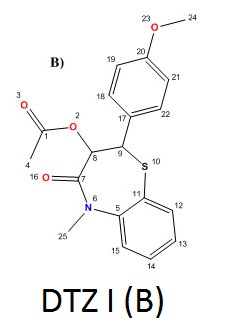
........

 .
.
NOTE DTZ (A) IS DILTIAZEM AND OTHER TWO ARE IMPURITIES

Structure elucidation of DTZ-I impurity
In the positive mass spectra, the protonated [M+H]+ molecular ion was detected at m/z 358.1. The even m/z number of [M+H]+ ions suggest that DTZ-I contains odd number of nitrogen atoms (nitrogen rule). From these results the molecular ion of DTZ-I was found to be at m/z 357. The mass difference between Diltiazem and DTZ-I was found to be 57 amu less. The positive HR-MS spectrum showed protonated molecular ion at m/z 358.1102 corresponding to molecular formula C19H20NO4S. When compared with the molecular formula of Diltiazem, there was a difference of C3H7N. The difference can be rationalized in terms of the loss of N, N-dimethylethanamine moiety. The presence of additional methyl signal at δ 3.38 ppm in 1H NMR (Figure 3) and corresponding carbon signal at 35.872 ppm in 13C NMR (Figure 4), The correlation between the carbon and proton clearly observed in HSQC (Figure 5) and no methylene protons were observed in HSQC. The methyl proton at δ 3.38 ppm showed HMBC (Figure 6) correlations for carbon C5 and C7 positions at 146.223 and 166.518 ppm respectively (Figure 7). The methyl proton at δ 3.38 ppm didn’t show any correlation in COSY (Figure 8), which confirms the N-Methyl in the structure. NMR assignments are shown in Table 1. The above spectral data supports the assigned structure as 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b][1,4]thiazepin-3-yl acetate (DTZ-I).






FOLLOW OTHERS IN .........http://www.orientjchem.org/vol31no3/analytical-characterization-of-two-new-related-impurities-of-diltiazem-by-high-resolution-mass-spectrometry-and-nmr-techniques/
1Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Limited, API Plant-III, Medak District, Hyderabad 500072, Telangana, India. 2Centre for chemical sciences & Technology, Institute of Science and Technology, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Hyderabad, Kukatpally, Hyderabad 500085, Telangana, India. Corresponding author E-mail: jagadeeshn@drreddys.com
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojc/310363
ABSTRACT: Diltiazem (DTZ) is an optically active calcium channel blocker having a benzodiazepine structure. Two impurities (referred as DTZ-I and DTZ-II) were detected with area percentages ranging from 0.1% to 0.15% during the impurity profile study of Diltiazem hydrochloride drug substance. A simple isocratic high performance liquid chromatographic method (HPLC) and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) were used for the detection. The impurities were isolated by preparative column chromatography. Analytical information from nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectral data of the potential impurities revealed their structures as 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b][1,4]thiazepin-3-yl acetate (DTZ-I) and 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-5-vinyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b][1,4]thiazepin-3-yl acetate (DTZ-II). Impurity identification, isolation and structure elucidation were discussed.
KEYWORDS: Diltiazem; Potential impurities; Isolation; characterization techniques
Copy the following to cite this article:
Jagadeesh N, Ravindrakumar Y, Mohanty S, Srinivasarao T, Jayashree A. Analytical Characterization of two new related impurities of Diltiazem by High Resolution Mass spectrometry and NMR techniques. Orient J Chem 2015;31(3).
//////////
DILTIAZEM IS

//////////////'
JHANSI, INDIA

















View of Antiya Talaab












///////
NOTE DTZ (A) IS DILTIAZEM AND OTHER TWO ARE IMPURITIES
Structure elucidation of DTZ-I impurity
In the positive mass spectra, the protonated [M+H]+ molecular ion was detected at m/z 358.1. The even m/z number of [M+H]+ ions suggest that DTZ-I contains odd number of nitrogen atoms (nitrogen rule). From these results the molecular ion of DTZ-I was found to be at m/z 357. The mass difference between Diltiazem and DTZ-I was found to be 57 amu less. The positive HR-MS spectrum showed protonated molecular ion at m/z 358.1102 corresponding to molecular formula C19H20NO4S. When compared with the molecular formula of Diltiazem, there was a difference of C3H7N. The difference can be rationalized in terms of the loss of N, N-dimethylethanamine moiety. The presence of additional methyl signal at δ 3.38 ppm in 1H NMR (Figure 3) and corresponding carbon signal at 35.872 ppm in 13C NMR (Figure 4), The correlation between the carbon and proton clearly observed in HSQC (Figure 5) and no methylene protons were observed in HSQC. The methyl proton at δ 3.38 ppm showed HMBC (Figure 6) correlations for carbon C5 and C7 positions at 146.223 and 166.518 ppm respectively (Figure 7). The methyl proton at δ 3.38 ppm didn’t show any correlation in COSY (Figure 8), which confirms the N-Methyl in the structure. NMR assignments are shown in Table 1. The above spectral data supports the assigned structure as 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b][1,4]thiazepin-3-yl acetate (DTZ-I).
FOLLOW OTHERS IN .........http://www.orientjchem.org/vol31no3/analytical-characterization-of-two-new-related-impurities-of-diltiazem-by-high-resolution-mass-spectrometry-and-nmr-techniques/
Analytical Characterization of two new related impurities of Diltiazem by High Resolution Mass spectrometry and NMR techniques096
Jagadeesh Narkedimilli1,2,*, Y. Ravindrakumar1 ,Sandeep Mohanty1, T. Srinivasarao1, A. Jayashree21Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Limited, API Plant-III, Medak District, Hyderabad 500072, Telangana, India. 2Centre for chemical sciences & Technology, Institute of Science and Technology, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Hyderabad, Kukatpally, Hyderabad 500085, Telangana, India. Corresponding author E-mail: jagadeeshn@drreddys.com
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojc/310363
ABSTRACT: Diltiazem (DTZ) is an optically active calcium channel blocker having a benzodiazepine structure. Two impurities (referred as DTZ-I and DTZ-II) were detected with area percentages ranging from 0.1% to 0.15% during the impurity profile study of Diltiazem hydrochloride drug substance. A simple isocratic high performance liquid chromatographic method (HPLC) and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) were used for the detection. The impurities were isolated by preparative column chromatography. Analytical information from nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectral data of the potential impurities revealed their structures as 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b][1,4]thiazepin-3-yl acetate (DTZ-I) and 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-5-vinyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b][1,4]thiazepin-3-yl acetate (DTZ-II). Impurity identification, isolation and structure elucidation were discussed.
KEYWORDS: Diltiazem; Potential impurities; Isolation; characterization techniques
Copy the following to cite this article:
Jagadeesh N, Ravindrakumar Y, Mohanty S, Srinivasarao T, Jayashree A. Analytical Characterization of two new related impurities of Diltiazem by High Resolution Mass spectrometry and NMR techniques. Orient J Chem 2015;31(3).
//////////
DILTIAZEM IS

//////////////'
JHANSI, INDIA












View of Antiya Talaab











///////