
Acting on actin: The mechanism of action of amphidinolide X and amphidinolide J, two relatively small cytotoxic macrolides, has been elucidated. They do not target microtubules and intermediate filaments. The effects observed in A549 and PtK2 cells and the in vitro interaction with actin monomer (G-actin) indicate that these macrolides behave as actin-assembly inhibitors.
Mechanism of Action of the Cytotoxic Macrolides Amphidinolide X and J
DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201100042
Author Information
Email: Prof. Dr. Jaume Vilarrasa (jvilarrasa@ub.edu), Dr. J. Fernando Díaz (i.barasoain@cib.csic.es), Dr. Isabel Barasoain (fer@cib.csic.es)
*Departament de Química Orgànica, Facultat de Química, Universitat de Barcelona, Diagonal 647, 08028 Barcelona (Spain)
Corrected by:Corrigendum: Corrigendum: Mechanism of Action of the Cytotoxic Macrolides Amphidinolide X and J
Vol. 12, Issue 9, 1293, Version of Record online: 9 JUN 2011
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cbic.201100042/abstract
Vol. 12, Issue 9, 1293, Version of Record online: 9 JUN 2011
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cbic.201100042/abstract
Others
Total Synthesis by Alkene Metathesis: Amphidinolide X (Urpí /Vilarrasa),
To assemble the framework of the cytotoxic macrolide Amphidinolide X (3), Fèlix Urpí and Jaume Vilarrasa of the Universitat de Barcelona devised (Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 5191. DOI: 10.1021/ol8021676) the ring-closing metathesis of the alkenyl silane 1. No Ru catalyst was effective, but the Schrock Mo catalyst worked well.Total Synthesis of Amphidinolide X & Y
Fürstner
A. Fürstner, E. Kattnig, O. Lepage, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9194-9204.DOI: 10.1021/ja061918e

Another pair of amphidinolides in the bag, Fürstner et al. have completed the synthesis of X (the only member of the series with an even-numbered macrocycle) and Y using a powerful iron catalysed process. Both products (as with most of the family) are cytotoxic, and contain the heavily functionalised THF moiety. This allowed the group to create an intermediate common to both campaigns, starting from a simple epoxide produced from an Sharpless epoxidation.

This portion of the natural product was coupled using an alkyl Suzuki reaction to the rest of the molecule in both cases, along with macrolactonisation to furnish the major ring system. In amphidinolide Y, a boron-mediated aldol reaction was used to create the 1,4 anti relationship between a pair of hydroxyls in the C1 - C12 fragment, in a 4:1 dr. Inseparable at this point, they carried the mixture through to a diastereoselective methyl grignard addition.


Figure 1: Scheme 1. (A) Sharpless asymmetric epoxidation of allylic alcohols 1 mediated by Ti(IV)-diethyltartrate (DET) catalyst with alkyl hydroperoxide as terminal oxidant leading to enantioenriched epoxides 2. (B) Preferential attack of the oxygen atom as a function of the stereochemistry of the DET chiral ligand. (C) Schematic representation of the dimeric active catalytic species 3.

Figure 10: Scheme 10. Structure of amphidinolide X 35 and details of the SAE step.
PAPER

http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.200900865/abstract
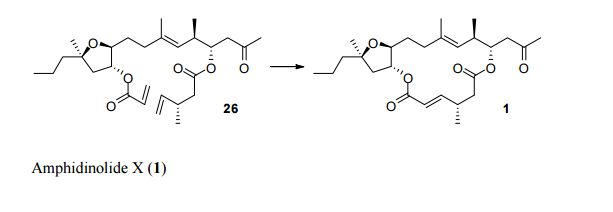
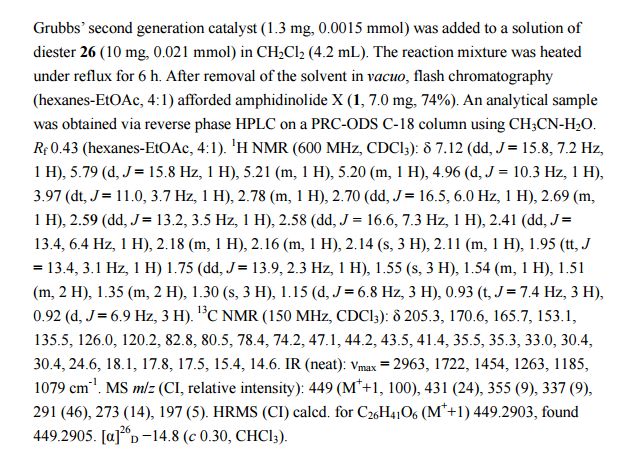
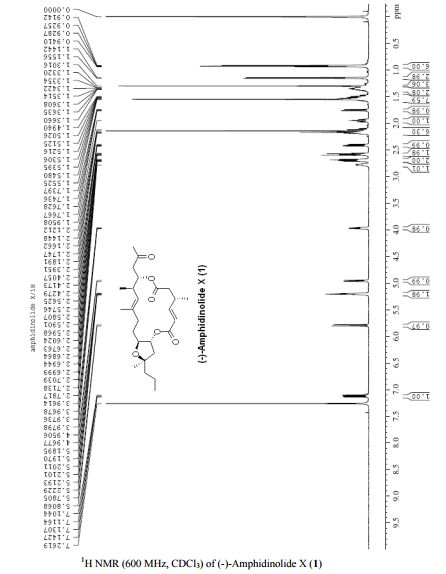
PAPER

http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/chem.200802069/abstract
////////////Cytotoxic Macrolides, Amphidinolide X and J
/////////
port louis FOOD, MAURITIUS




/////////







