Zhong-Xia WANG
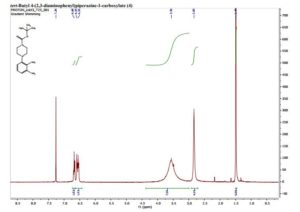
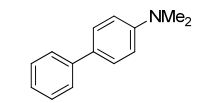
N,N-dimethyl-4-biphenylamine
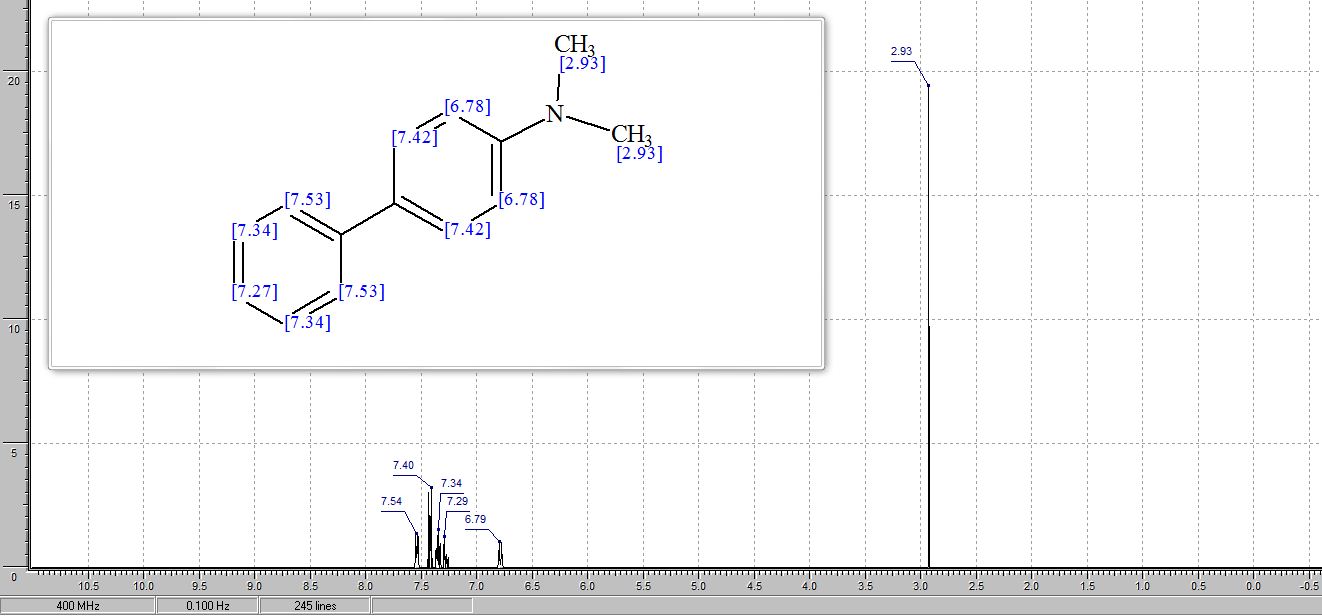
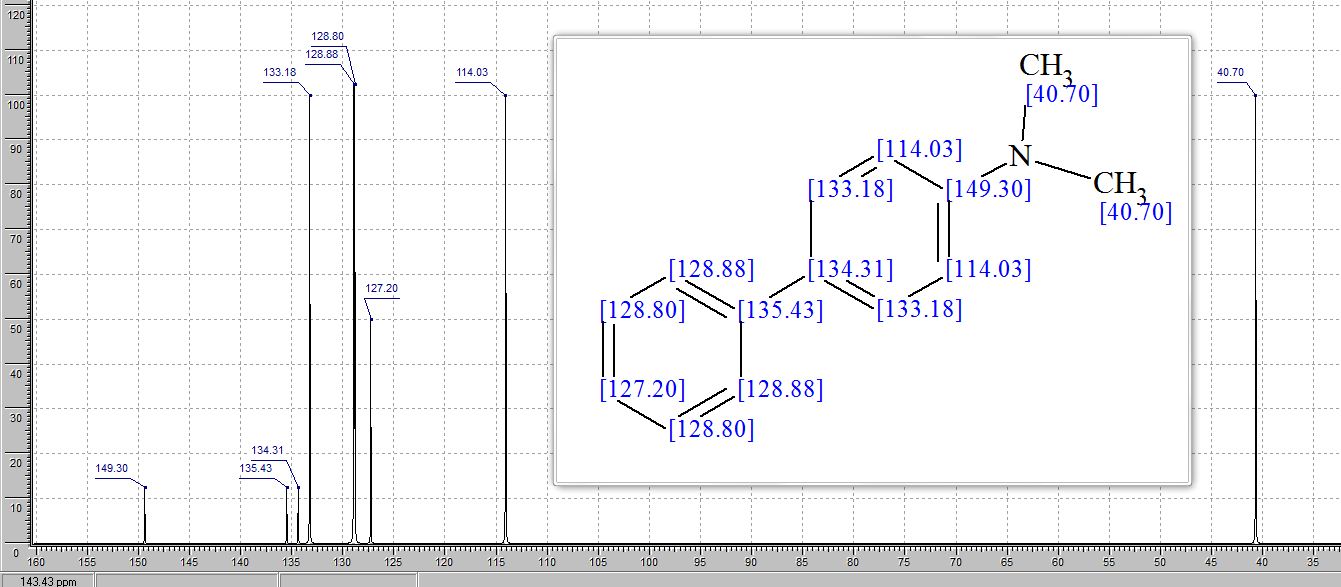
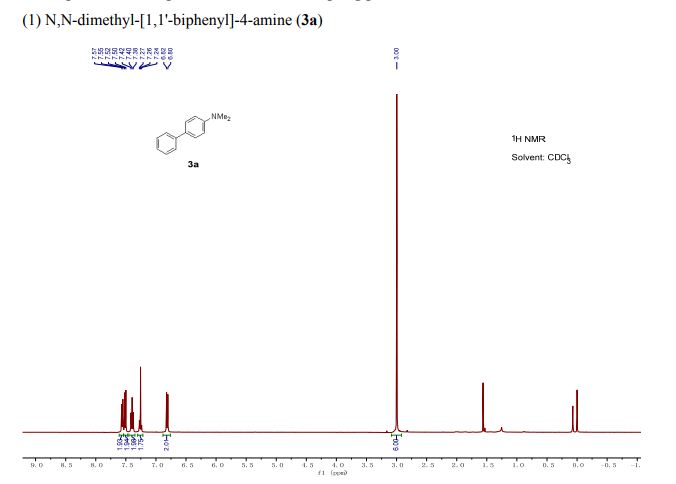
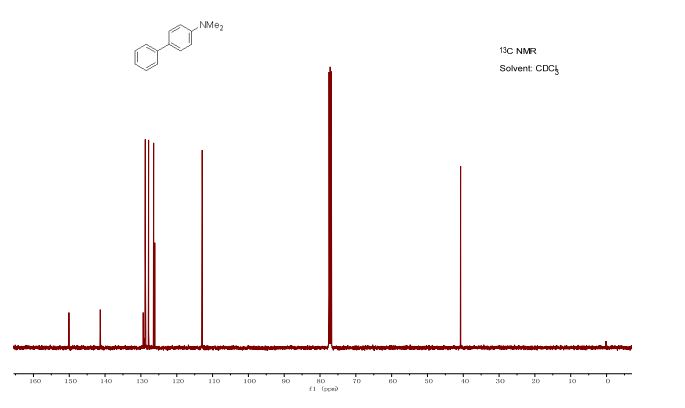
(1) N,N-dimethyl-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-amine (3a) 5,6
Elute: EtOAc/petroleum ether: 1/100 (v/v), white solid, yield 97.8 mg (99%).
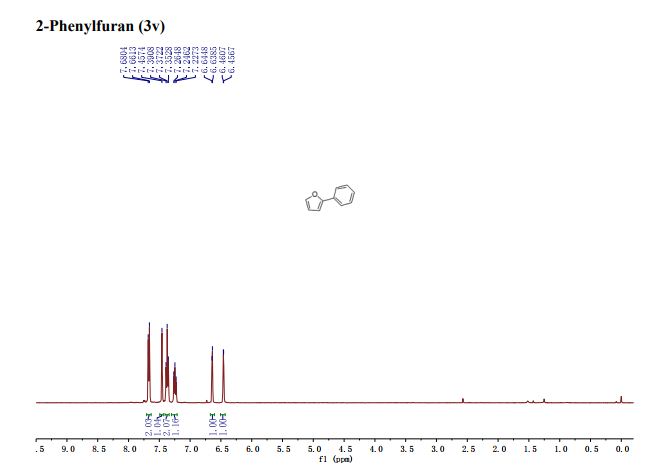
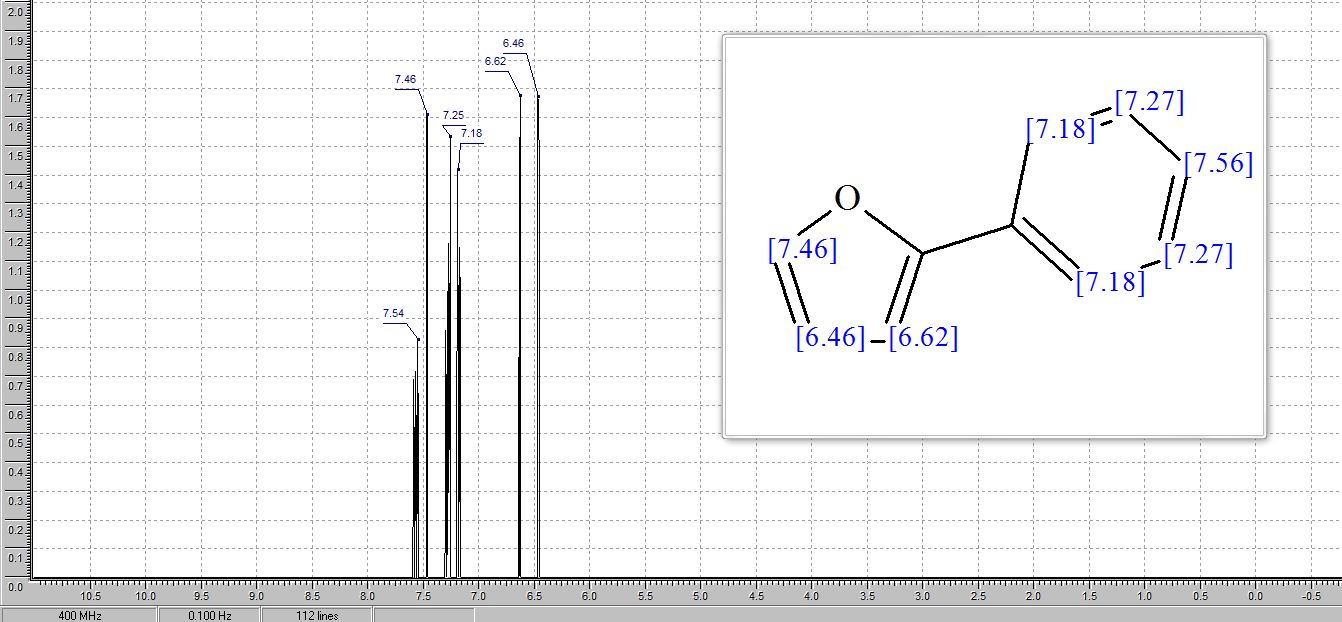
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.56 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.51 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.40 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 7.30–7.21 (m, 1H), 6.81 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 3.00 (s, 6H).
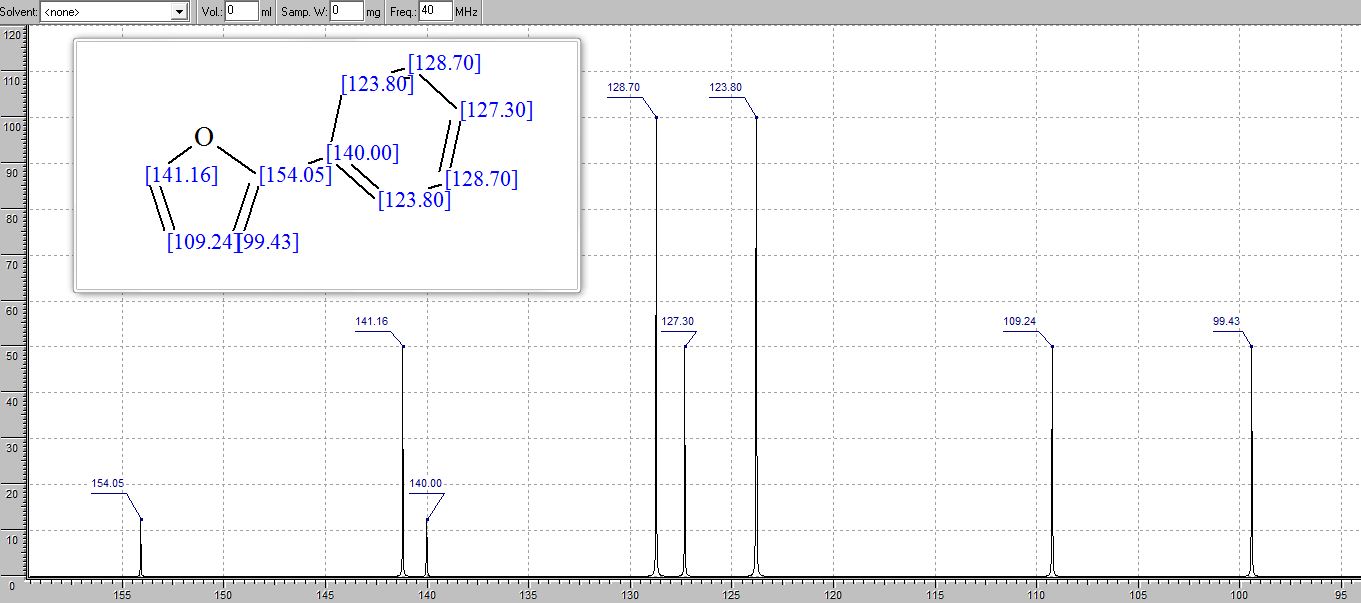
13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3): δ 150.09, 141.34, 129.37, 128.78, 127.84, 126.43, 126.12, 112.90, 40.97.
5 Yang, X.; Wang, Z.-X. Organometallics 2014, 33, 5863.
(6) Stibingerova, I.; Voltrova, S.; Kocova, S.; Lindale, M.; Srogl, J. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 312.
Transition-Metal-Free Cross-Coupling of Aryl and Heteroaryl Thiols with Arylzinc Reagents
† CAS Key Laboratory of Soft Matter Chemistry, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at Microscale and Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230026, P. R. China
‡ Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin 300072, P. R. China
Org. Lett., Article ASAP
DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b03145
*E-mail: zxwang@ustc.edu.cn.
Abstract
Cross-coupling of (hetero)arylthiols with arylzinc reagents via C–S cleavage was performed under transition-metal-free conditions. The reaction displays a wide scope of substrates and high functional-group tolerance. Electron-rich and -deficient (hetero)arylthiols and arylzinc reagents can be employed in this transformation. Mg2+ and Li+ ions were demonstrated to facilitate the reaction.
In summary, we developed a transition-metal-free coupling reaction of (hetero)arylthiols with arylzinc reagents to form bi(hetero)aryls. The reaction exhibited wide substrate scope and good compatibility of functional groups. Electron-rich and -poor aryl or heteroaryl thiols can be converted. Various arylzinc reagents, including electron-rich and electron-poor reagents, can be employed as the coupling partners. Preliminary mechanistic studies suggest a nucleophilic aromatic substitution pathway, and Mg2+ and Li+ ions play important roles in the process of reaction. This study provides an example of S2– as a leaving group in an aromatic system and an effective methodology for the synthesis of bi(hetero)aryls including pharmaceutical molecules without transition-metal impurities.
Zhong-Xia WANG
|
Zhong-Xia Wang is a professor in the Department of Chemistry at the University of Science and Technology of China. He received his BS degree (1983) and MS degree (1986) from Nankai University, and PhD degree (1997) from the University of Sussex, UK. Since July 1986, Wang has been working at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) successively as Assistant, Lecturer, Associate Professor, and Professor. From Aug. 1993 to Oct. 1996, he pursued his doctoral studies at the University of Sussex, UK, and from Oct. 1999 to Oct. 2000, he was a Research Associate at the Chinese University of Hong Kong.学 系 Department of Chemistry Predicts
////////////



 学 系
学 系