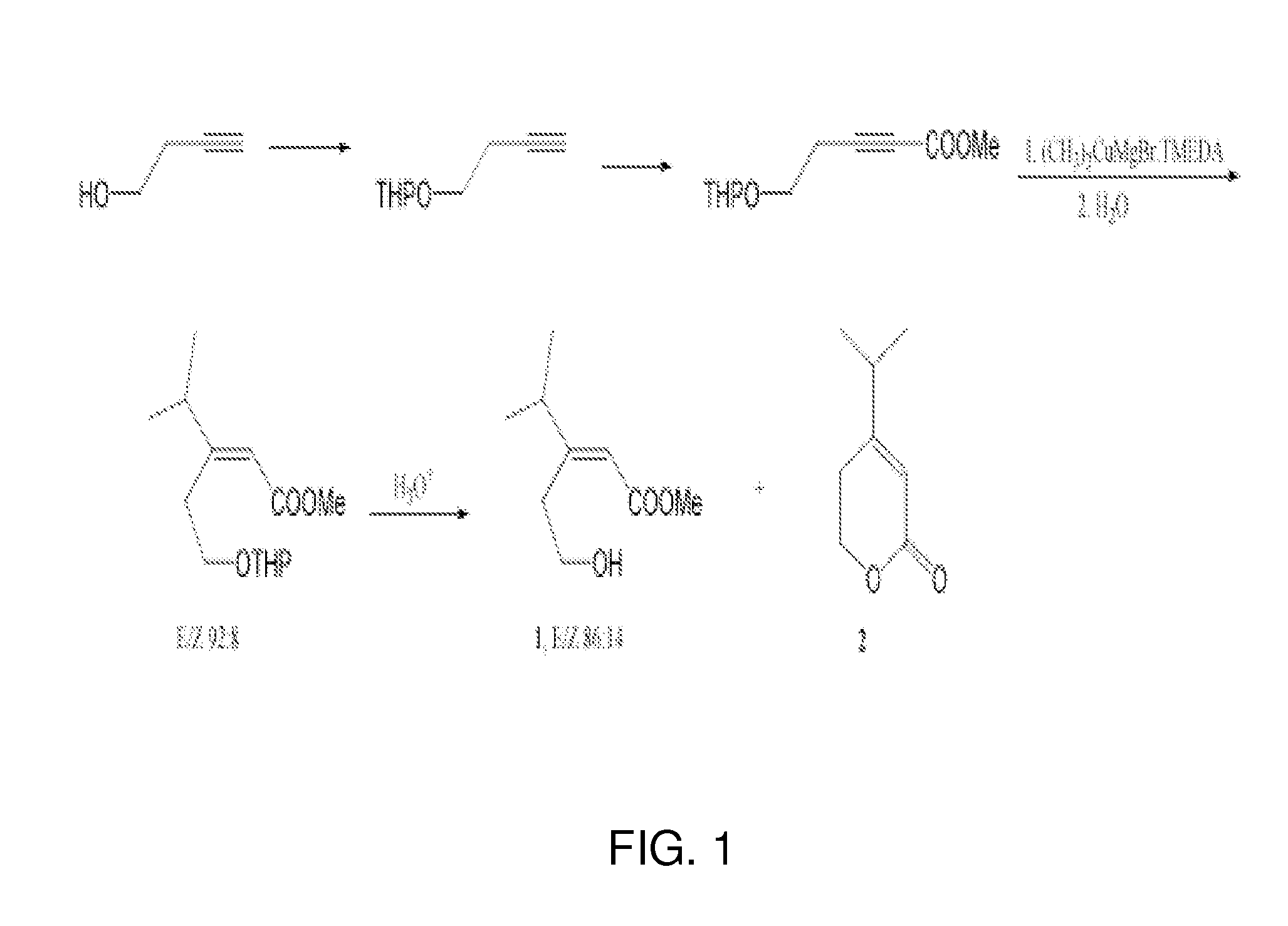
1= methyl (E)-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-2-pentenoate+methyl (E)-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-2-pentenoate
2=LACTONE
an unsaturated hydroxy ester pheromone collected from the headspace and feces of male Diaprepes abbreviatus was isolated, identified and synthesized. The pheromone, methyl (E)-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-2-pentenoate, was discovered by gas chromatography-coupled electroantennogram detection (GC-EAD) and identified by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). The synthetic protocol yielded a 86:14 mixture of methyl (E)-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-2-pentenoate and an inactive methyl (Z)-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-2-pentenoate along with a lactone decomposition product. The activity of the synthetic E isomer was confirmed by GC-EAD, GC-MS, NMR and behavioral assays. No antennal response was observed to the Z isomer or the lactone. In a two-choice olfactometer bioassay, female D. abbreviatus moved upwind towards the synthetic pheromone or a source of natural pheromone more often as compared to clean air. Males showed no clear preference for the synthetic pheromone.
The root weevil Diaprepes abbreviatus (L.), is a major pest of citrus in the Caribbean and Florida. Prior to the 1960's, D. abbreviatus was reported only in the Caribbean. Because multiple phenotypic populations occur on Puerto Rico it is suggested that D. abbreviatus originated in Puerto Rico (Lapointe 2004). Since its discovery near Apopka, Fla. in 1964, it has spread to Louisiana, Texas and California. There is no geographic or climatic barrier to prevent the southern movement of this insect to Mexico, Mesoamerica and South America (Lapointe et al. 2007).
This migration is of concern because this insect is destructive. Adult beetles of D. abbreviatus oviposit and feed on leaves of a wide range of hosts including more than 270 species of plants in 59 plant families. Feeding by adults on leaves causes a characteristic notching pattern; however, the larval stage causes the most serious damage. Neonate larvae fall to the ground and burrow into the soil where they feed on progressively larger roots over a period of months as they grow. Larval feeding on citrus tree roots can eventually girdle the crown area of the root system, killing the host plant. When larval development is completed, adults emerge from the soil to feed upon foliage where aggregation, mating and oviposition take place. In certain citrus growing areas, root damage by larval D. abbreviatus creates favorable conditions for species ofPhytophthora, a very serious and often lethal plant pathogen, to invade roots and further hasten the decline of trees.
In Florida, citrus growers spend up to $400/acre for combined control of D. abbreviatus and Phytophthora. In 2009, it was estimated that the total increase in costs per ton due to the establishment and spread of Diaprepes root weevil in California would be $53.60 for orange, $45.20 for grapefruit, $42.50 for lemon and $200.00 for avocado. In view of the negative economic impact caused by the feeding of this insect and in view of the fact that there appear to be no natural barriers to important agricultural citrus growing areas, attractants that will allow for the monitoring, tracking, trapping and destroying of this insect have been sought.
Diaprepes abbreviatus has been placed in the subfamily Entiminae of the Curculionidae (Marvaldi et al. 2002) Within the superfamily Cu rculionoidea (weevils) the majority of attractants or pheromones identified to date are long-range, male-produced aggregation pheromones (Seybold and Vanderwel 2003, Ambrogi et al. 2009). Aggregation of D. abbreviatus adults and the occurrence of so-called “party trees” have been observed (Wolcott 1936). Schroeder (1981) suggested a male-produced pheromone attracted females and a female-produced pheromone attracted males. Beavers et al. (1982) showed in laboratory tests that male and female D. abbreviatus were significantly attracted to the frass of the opposite sex. Jones and Schroeder (1984) demonstrated a male-produced pheromone in the feces that attracted both sexes. A pheromone responsible for arrestment behavior was suggested by Lapointe and Hall (2009). U.S. Pat. No. 8,066,979 to Dickens et al. showed for the first time that D. abbreviatus adults have olfactory receptors for secondary plant metabolites that belong to diverse chemical groups: (a) alcohol and aldehyde monoterpenes (e.g., linalool, citronellal, nerol, and trans-geraniol), (b) green leaf volatiles (e.g., cis-3-hexen-1-ol and trans-2-hexen-1-ol), and (c) an aromatic monoterpenoid (e.g., carvacrol). Otálora-Luna et al. (2009) identified by gas-chromatograph electroantennograph detection (GC-EAD) a number of plant volatiles from citrus leaves that elicited antennal response in D. abbreviatus. Such kairomones may act in concert with a pheromone to attract conspecifics to a suitable food source (Dickens 1990). Only one pheromone, that of Sitona lineatus (4-methyl-3,5-heptanedione), an aggregation pheromone, has been isolated from the Entiminae (broad-nosed weevils) (Blight et al. 1984). Blight and Wadhams (1987) suggested that S. lineatus produces its aggregation pheromone in the spring and that the pheromone activity is synergized by host plant volatiles including (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol and linalool.
chromatographed again with hexanes/ethyl acetate/MeOH, 16:6:1 to furnish 1 (E/Z 86:14, approximately 90 mg, approximately 58%) in the less polar fraction.
1H NMR (600 MHz, C6D6, 6): 0.79 (d, J=6.6 Hz, (CH3)2, a 0.91 (d, J=6.6 Hz, (CH3)2, Z), 2.01-2.08 (m, H-4 E, CH2C═C, Z), 2.46 (t, J=5.4 Hz, OH, E), 2.76 (t, J=6.6 Hz, CH2C═C, E), 3.34 (s, OCH3, E), 3.36-3.38 (m, CH2OH, Z), 3.41 (s, OCH3, Z), 3.70 (q, J=5.4 Hz, CH2OH, E), 4.32 (septet, H-4, Z), 5.71 (br. s, H-2, Z), 5.80 (br. s, H-2, E).
13C NMR (151 MHz, C6D6, E isomer): 21.7 (two carbons), 35.6, 36.7, 51.1, 62.5, 115.6, 167.7, 168.7; Z isomer: 20.9 (two carbons), 29.8, 35.1, 50.8, 61.6, 116.0, 165.7, 166.8.
Lactone 2 (approximately 10 mg) was recovered from the more polar (second) fraction. GC-MS (m/z, relative intensity): 140 (M+, 16), 125 (7), 110 (15), 97 (19), 96 (59), 95 (96), 82 (24), 81 (100), 67 (73), 55 (17), 41 (40). 1H NMR (400 MHz, C6D6, 6): 0.57 (d, J=6.6 Hz, (CH3)2), 1.37 (br. t, J=6.5 Hz, CH2C═), 1.70 (septet, J=6.6 Hz, CH(CH3)2), 3.61 (t, J=6.5 Hz, CH2O), 5.67 (d, J=1.0 Hz, CHC═). NMR data are in agreement with ones obtained for this compound in CDCl3 (D'Annibale et al. 2007).
| TABLE 1 |
|
| HMBC and NOESY NMR spectroscopic data for the putative |
| pheromone of Diaprepes abbreviatus in CDCl3 |
 |
|
| | | J coupling | | |
| δ 13C | δ 1H | constants | HMBC | |
| Position | [ppm] | [ppm] | [Hz] | correlations | NOESY |
|
| 1 | 169.0* | — | — | — | — |
| 2 | 115.5 | 5.83 | s | | 1.10 |
| 3 | 166.9* | — | — | — | — |
| 4 | 36.35* | 2.43 | m J = 6.7 | | |
| 5 and 6 | 21.7 | 1.10 | d, J = 6.8 | C4, C3 | 5.83 |
| | | | | and |
| | | | | 2.84 |
| 7 | 35.2 | 2.84 | t, J = 6.4 | C2, C3, C4, | 1.10 |
| | | | C8 | |
| 8 | 62.5 | 3.8 | br t J = 6.3 | | — |
| 9 | 51.7 | 3.7 | s | Cl |
|
| 1H (600 MHz), 13C (151 MHz),. |
| Chemical shifts referenced to δ(CHCl3) = 7.26 ppm for 1H and δ(CHCl3) = 77.36 ppm for 13C. |
| Coupling constants are given in Herzt [Hz]. |
| *The 13C chemical shifts are deduced from HMBC; others are deduced from HSQC. |
| 1H chemical shifts are deduced from 1D 1H NMR |
lactone 2
| TABLE 2 |
|
| 1H (600 MHz) and 13C (151 MHz) spectroscopic data for |
| the lactoneinactive degradation product of the putative |
| pheromone of Diaprepes abbreviatus found in |
| headspace collections |
 |
|
| | δ 1H |
| .Position | δ 13C [ppm] | [ppm] |
|
| 2 | 114.08 | 5.80 |
| 4 | 34.8 | 2.47 |
| 5 and 6 | 20.2 | 1.12 |
| 7 | 26.4 | 2.39 |
| 8 | 66.3 | 4.36 |
|
| Only HSQC data are reported for the lactone. |
| Chemical shifts referenced to δ(CHCl3) = 7.26 ppm for 1H and δ(CHCl3) = 77.36 ppm for 13C. |