
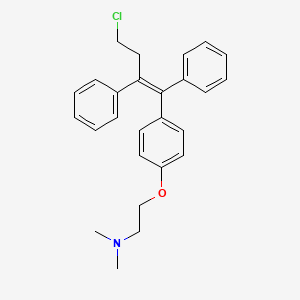
Toremifene
2-[4-[(Z)-4-chloro-1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl]phenoxy]-N,N-dimethylethanamine
(Z)-2-[4-(4-Chloro-1,2-diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy]-N,N-dimethylethanamine
(Z)-4-Chloro-1,2-diphenyl-1-[4-[2-(N,N-dimethylamino)ethoxy]phenyl]-1-butene
(Z)-Toremifene
2-({4-[(1Z)-4-chloro-1,2-diphenylbut-1-en-1-yl]phenyl}oxy)-N,N-dimethylethanamine
4-chloro-1,2-diphenyl-1-[4-[2-(N ,N-dimethylamino)ethoxy]phenyl]-1-butene
Toremifene; Acapodene; Farestone; Z-Toremifene; Toremifeno; Toremifenum
| Molecular Formula: |
C26H28ClNO |
| Molecular Weight: |
405.95962 g/mol |
cas 89778-26-7
Launched – 1988.Orion (FI), greast cancer
- Citrate, Toremifene, GTx-006
NK-622
- Fareston
- FC 1157a
- FC-1157a
- FC1157a
- Toremifene
- Toremifene Citrate
- Toremifene Citrate (1:1)
- Toremifene, (E)-Isomer
-
- C26H28ClNO · C6H8O7
- Molecular Weight 598.08
 Toremifene Citrate
Toremifene Citrate
Toremifene is a first generation selective estrogen receptor
modulator (SERM). Like TAMOXIFEN, it is an estrogen agonist for bone
tissue and cholesterol metabolism but is antagonistic on mammary and
uterine tissue.
The company GTx is conducting phase III clinical trials for the
prevention of prostate cancer in men who have been diagnosed with high
grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN).
Toremifene citrate is an oral
selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) which helps oppose the actions of
estrogen in the body. Licensed in the United States under the brand name
Fareston, toremifene citrate is
FDA-approved for use in advanced (
metastatic)
breast cancer. It is also being evaluated for prevention of
prostate cancer under the brand name
Acapodene.
[1]

In 2007 the pharmaceutical company
GTx, Inc was conducting two different phase 3
clinical trials; First, a pivotal Phase clinical trial for the treatment of serious side effects of
androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) (especially vertebral/spine fractures and
hot flashes, lipid profile, and
gynecomastia)
for advanced prostate cancer, and second, a pivotal Phase III clinical
trial for the prevention of prostate cancer in high risk men with high
grade
prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, or PIN. Results of these trials are expected by first quarter of 2008
[2]
An NDA for the first application (relief of prostate cancer ADT side effects) was submitted in Feb 2009,
[3] and in Oct 2009 the FDA said they would need more clinical data, e.g. another phase III trial.
[4]
Originally developed at Orion, toremifene was subsequently licensed
to Nippon Kayaku in Japan and to Asta Medica (now, part of Meda) in
Germany.
Synthesis

……….
PATENT
http://www.google.com/patents/CN104230723A?cl=en
Toremifene (Toremifene), chemical name (Z)
-4- chloro-1,2-diphenyl–1- [4- (2- (N, N- dimethylamino) ethoxy yl)
phenyl] -1-butene, having the structure I.Toremifene
to tamoxifen (Tamoxifen) analogues with anti-estrogenic activity, can
be used in the treatment of hormone-dependent breast cancer, and its
E-isomer has the presence of estrogenic activity, E isomers toremifene
may counteract anti-estrogenic activity, and therefore isomeric purity
is essential toremifene.Toremifene was
developed in 1983 by the Finnish Famos company, listed in 1996 by the
Orion company in the EU, the trade name Fareston, 2002 to enter the
country, the trade name of toremifene.
RJ Toivola et al., European Patent EP95875,
disclosed in U.S. Patent US4696949A synthetic route toremifene, that
following a synthetic route, the synthetic route to phenol as a raw
material, by acylation, rearrangement, alkyl group and an addition
reaction to give 1,2-diphenyl -1- [4- [2- (N, N- dimethylamino)
ethoxyphenyl]] – 1,4-diol (Compound 5) as the key intermediate, further
HCl in ethanol or hydrochloric acid elimination reaction occurs, then
get toremifene thionyl chloride reaction. The
main problem with this approach is that the elimination reaction of the
compound 5 in ethanol occurs when hydrochloric acid or concentrated
hydrochloric acid, the resulting triaryl alcohol butyrate (Compound 6)
having a Z / E configuration, both the ratio of 1: 2 ~ 2: 1, stereo
selectivity is not high, and there are 5% of the cyclization by-product;
on the Z / E configuration Miyoshi butyric fractional crystallization
of alcohol, you can get pure Z-type Miyoshi butyric alcohol , but the
yield is only 41%; then, Z-type Miyoshi butyric alcohol chlorination
reaction occurs in the action of thionyl chloride, the purified product
toremifene.
U.S. Patent US5491173A also reported another synthetic route toremifene namely the following two synthetic routes. The
route to the aryl ketone (Compound 7) with a phenyl Grignard reagent
addition reaction of ketone carbonyl groups to give triaryl-butanediol
(compound 5), which is the elimination of toremifene and chlorinated
reaction products happen again.
Chinese Patent Publication No. CN1125716A
application reported an efficient synthesis of Z-type Miyoshi butyric
alcohol (compound 6) method, US4696949A compared with the US patent, the
method mild conditions, reduce the acid concentration and reaction
temperature, reaction time, triarylphosphine butanediol (Compound 5) in
concentrated hydrochloric acid or concentrated hydrochloric isopropanol
or ethanol effect of concentrated hydrochloric acid, can be 60-78%
selectivity and 95% yield of type 2 Miyoshi butyric alcohol But after
Publication No. 0 02,126,969 attached eight patent applications after
the inventor repeated experiments show that the technique disclosed in
the patent application programs can not achieve their claimed technical
effect.
Publication No. CN102126969A of Chinese
patent applications through the intermediate Miyoshi butyric alcohol
occurs at a catalytic converter configuration of concentrated
hydrochloric acid, while taking advantage of differences in solubility,
so E- type Miyoshi butyric alcohol continuously into Z-type Miyoshi
butyric alcohol (compound 6) precipitates, thereby undermining the
balance, so that one of the E-type Miyoshi butyric alcohol continuously
into Z-type Miyoshi butyric alcohol (compound 6) to give the Z-Miyoshi
butyric alcohol ( Compound 6) and then get toremifene thionyl chloride
after chlorination. Although to some extent, improve the yield, but increased operating procedure, is not conducive to industrial production.
Currently, the key intermediate is patent protected, and z-type
Miyoshi butyric alcohol (compound 6) stereoselective low yield and
isolated intermediates, to solve this problem, to overcome technical
barriers to foreign pharmaceutical companies, urgent need to find a
simple process, low cost, easy to separate and viable for large-scale
production of synthetic routes.
To achieve the above object, according to
one aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method of
synthesizing toremifene, synthetic method comprising: a step S1, so that
a compound having the structural formula II with a compound B having
the structural formula III C occurs Mike Murray to give compound D
having the structural formula IV; step S2, the Compound D and Compound E
or Compound E of the hydrochloride salt of the formula V having a
phenolic hydroxyl group on the occurrence of a selective alkylation
reaction, to give a compound having the structural formula VI F; step
S3, the compound F is reacted with thionyl chloride to give toremifene,
wherein,
Formula II is:
Structural formula III as follows:
Formula IV is
Of formula V is C1CH2CH2N (CH 3) 2; formula VI is
FIG. 1 illustrates the present invention obtained in Example 1 H NMR spectrum of compound D of implementation;
 FIG. 2 shows the 1 H NMR spectrum of the present invention, the compound obtained in Example F;
FIG. 2 shows the 1 H NMR spectrum of the present invention, the compound obtained in Example F;
 FIG. 3 shows the present invention is a proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of toremifene obtained in Example.
FIG. 3 shows the present invention is a proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of toremifene obtained in Example.

Figure 1, which shows a spectrum of results for Che bandit? (400 cm
take, 01 ^ 0) 3 = 9.20 (! 8,1 1), 7.37 (^ = 7.4 to take, 2 1!), 7.30- 7.
23 (m, 3H), 1.22- 7. 15 (m, 2H), 7. 15 – 7. 06 ( m, 3H), 6. 61 (dd, J =
9. 0, 2. 2Hz, 2H), 6. 49 -. 6. 32 (m, 2H), 4 48 (s, 1H), 3 30 (. m,
2H), 2 55 (t, J = 7. 5Hz, 2H);. F proton nuclear magnetic resonance
spectrum of the compound attached to the
Figure 2, showing spectrum results Che NMR (400MHz, DMSO) δ = 7. 36
(d, J = 7. 3Hz, 2H), 7. 31 – 7. 25 (m, 3H), 7. 21 – 7. 10 (m, 5H), 6. 75
– 6. 69 (m , 2H), 6. 59 (d, J = 8. 8Hz, 2H), 4. 49 (s, 1H), 3. 88 (t, J
= 5. 8Hz, 2H), 3. 31 (d, J = 4. 3Hz, 2H), 2. 57 (t, J = 7.5Hz, 2H),
2.52 (t, J = 4.6Hz, 2H), 2 15 (s, 6H);.
Tommy remifentanil NMR hydrogen spectrum in Figure 3 attached,
showing spectrum results Che NMR (400MHz, CDC13) δ = 7. 41 -. 7. 33 (m,
2H), 7 29 (dt, J = 7. 1, 2. 9Hz, 3H), 7. 20 (dd, J = 10. 0, 4. 3Hz, 2H),
7. 13 (dd, J = 7. 1, 4. 3Hz, 3H), 6.87- 6. 72 (m, 2H), 6. 57 (dd, J =
6. 8, 4. 8Hz, 2H), 3. 92 (t, J = 5. 8Hz, 2H), 3. 41 (t, J = 7. 5Hz, 2H),
2. 92 (t, J = 7. 5Hz, 2H), 2. 63 (t, J = 5. 8Hz, 2H), 2. 28 (s, 6H).
The synthetic routes above synthetic method are as follows:
Synthesis of toremifene:
To a 2L reaction flask 1. 1L of toluene,
110g (0. 28mol) obtained in the above step Z configuration compound F,
mixed to obtain a sixth system, the cooling system to the sixth mixed
0~5 ° C , was slowly added dropwise 99. 93g (0. 84mol) thionyl chloride
addition was complete the formation of the seventh mixed system, the
mixed system was slowly warmed to a seventh ll〇 ° C, for 1 hour to
obtain a third product system, stop The third product heating and
cooling system to 15~25 ° C, the third product system slowly poured into
1L of water, adding NaOH solution to a pH 9~10 and get the second
system, the second in and a system for liquid separation, and the
resulting aqueous phase to obtain a second solution was extracted with
1L toluene extraction, the organic phase of the second extraction
solution and liquid separation were combined and concentrated to give
crude toremifene, the crude product was mass ratio of 1 : mixed solvent
of ethyl acetate and acetone 1 crystals to give 103. 7g toremifene
products.
Synthesis of toremifene:
[0062] To a 5L reaction flask 3. 3L of
toluene, 110g (0. 28mol) obtained in the above step Z configuration
compound F, mixed to obtain a sixth system, the cooling system to the
sixth mixed 0~5 ° C , was slowly added dropwise 33. 31g (0. 28mol)
thionyl chloride addition was complete the formation of the seventh
mixed system, the mixed system was slowly warmed to a seventh ll〇 ° C,
after the reaction for 6 hours to obtain a third product system, stop
The third product heating and cooling system to 15~25 ° C, the third
product system slowly poured into 1L of water, potassium carbonate
solution to a pH 9~10 and get the second system, the second and system
for liquid separation, and the resulting aqueous phase to obtain a
second solution was extracted with 1L ethyl acetate, the organic phase
after the second extraction solution and liquid separation were combined
and concentrated to give crude toremifene, the crude product was
quality ratio was crystallized from acetone to give 92. 2g toremifene
products.
Purity of toremifene following method:
[0107] to take the product, add the mobile
phase dissolved and diluted into 1ml of 1. Omg solution containing,
according to HPLC octadecylsilane bonded silica as a filler to square 1%
trifluoroacetic acetic acid aqueous solution (A) and acetonitrile (B)
as the mobile phase gradient elution (T = Omin 10% B; T = lOmin 95% B; T
= 12min 100% B; T = 15min 10% B), detection wavelength 210nm; area
normalization method to calculate the Z configuration purity compound F,
where F Z configuration compound retention time of 6. 76min. The
purity of the above calculation or Z configuration detection obtained
compound D, compound D Z configuration and E configuration of the weight
ratio, toremifene yield and purity are reported in Table 1 below.
……………..
PATENT
http://www.google.com/patents/US5491173
c) 4-chloro-1,2-diphenyl-1-[4-[2-(N ,N-dimethylamino)ethoxy]phenyl]-1-butene (Z and E)
(Z)-isomer: The reaction is performed under dry conditions. 42.4 g of
(Z)-1,2-diphenyl-1-[4-[2-(N,N-dimethylamino
)ethoxy]phenyl]-1-buten-4-ol are dissolved in 250 ml of chloroform. Then
23.8 g of thionyl chloride areadded dropwise. The mixture is refluxed 3
h. The solvent is evaporated, after which the product is recrystallized
from ethyl acetate. The yield ofthe hydrochloride salt is 36.7 g (83%),
m.p. 194°-6° C. The base can be liberated from the Salt with 1M sodium
carbonate solution, after which the base is extracted in toluene. The
toluene solution is dried and the solvent is evaporated. The free base
has m.p. 108°-10° C. (from acetone).
1 H-NMR-spectrum (CDCl
3): δ 2.27 (6H, s), 2.63
(2H, t), 2.91 (2H, t), 3.41 (2H, t), 3.92 (2H, t), 6.54 (2H, d), 6.79
(2H. d), 7.15(5H, s), 7.31 (5H, s). MS: m/z 405/407 (M
+, 7/3), 72 (20), 58 (100).
The citric acid salt can be prepared as follows: 40.6 g of the
(Z)-isomer as a free base are dissolved in 175 ml of warm acetone and
24.3 g of citric acid are dissolved in 100 ml of warm acetone. The
solutions are combined and the mixture is allowed to cool. The citrate,
m.p. 160°-162° C., is collected by filtration.
(E)-isomer: The compound is prepared from (E)-1,2-diphenyl-1-[4-[2-(N
,N-dimethylamino)ethoxy]phenyl]-1-buten-4-ol in the same manner as the
corresponding (Z)-isomer. The hydrochloride salt is crystallized from
toluene. The yield is 35.8 g (81%) of a product having m.p. 183°-5° C.
The base can be liberated from the salt in the same manner as the
corresponding (Z)-isomer. It has m.p. 69°-71° C. (from hexane).
1 H-NMR-spectrum (CDCl
3): b 2.34 (6H, s), 2.74 (2H, t), 2.97 (2H,t), 3.43 (2H, t), 4.08 (2H, t), 6.80-7.30 (14H, m).
MS: m/z 405/407 (M
+, 7/3) 72 (19) 58 (100)
EXAMPLE 4
4-chloro-1,2-diphenyl-1-[4-[2-(N ,N-diethylamino)ethoxy]phenyl ]-1-butene (Z and E)
43.3 g of
1,2-diphenyl-1-[4-[2-(N,N-diethylamino)ethoxy]phenyl]butane-1,4-diol
(pureenantiomer pairs or their mixture: m.p. of (RR,SS)-pair is 107°-9°
C.)is suspended in 250 ml of toluene, after which 25ml toluene is
distilled off to dry the solution. The mixture is cooled to 0° C. with
stirring. While stirring and keeping the temperature at 0° C. or a
little below, 47.6 g of thionyl chloride of good qualityare added. The
mixture is stirred for 1 h at 0° C. and the temperature is then allowed
to rise to 22° C. The mixture is stirred at 80° C. until the reaction is
completed (about 3 h). After that, water is added to decompose the
excess of thionyl chloride followed by 20% sodium hydroxide solution to
liberate the product from itshydrochloride salt. The aqueous layer is
discarded and the toluene layer iswashed with water. Then the solvent is
evaporated to leave a mixture of (Z)- and (E)isomers (Z:E 7:3) as an
oil in quantitative yield.
(Z)-isomer: The (Z)-isomer is isolated from the isomer mixture above
as thehydrochloride salt because of the low melting point of the free
base. The m.p. of the hydrochloride salt is 178°-80° C. The
(Z)-isomermay be freed from its salt by any normal method.
1 H-NMR-spectrum (CDCl
3): δ 1.01 (6H, t), 2.57
(4H, q), 2.77 (2H, t), 2.91 t), 3.41 (2H, t), 3.90 t), 6.53 (2H, d),
6.78 (2H, d), 7.15 (5H, s), 7.31 (5H, s). (E)-isomer:
1 H-NMR-spectrum (CDCl
3): δ 1.07 (6H, t), 2.66 (4H, q), 2.89 (2H, t), 2.97 (2H, t), 3.42 (2H, t), 4.07 (2H, t), 6.90-7.20 (10H, m).
……………….
SEE
http://www.google.co.ug/patents/EP0095875B1?cl=en
………….

http://www.intechopen.com/books/topics-on-drug-metabolism/electrochemical-methods-for-the-in-vitro-assessment-of-drug-metabolism
References
- Price N, Sartor O,
Hutson T, Mariani S. Role of 5a-reductase inhibitors and selective
estrogen receptor modulators as potential chemopreventive agents for
prostate cancer. Clin Prostate Cancer 2005;3:211-4. PMID 15882476
- “GTx’s Phase III Clinical Development of ACAPODENE on Course Following Planned Safety Review” (Press release). GTx Inc. 2007-07-12. Retrieved 2006-07-14.
- “GTx Announces Toremifene 80 mg NDA Accepted for Review by FDA” (Press release).
- “GTx and Ipsen End Prostate Cancer Collaboration due to Costs of FDA-Requested Phase III Study”. 2 Mar 2011
///////





 LIONEL MY SON
LIONEL MY SON



