
Cas 1820758-44-8
C24 H18 F N3 O4 S
4′-((5-(2,3-Dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl-thio)-methyl)-4-fluorobiphenyl-2-carboxamide
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a constitutively active, ubiquitous serine/threonine kinase that takes part in a number of physiological processes ranging from glycogen metabolism to apoptosis. GSK-3 is a key mediator of various signaling pathways, such as the Wnt and the insulin/AKT signaling pathways.
Therefore, dysregulation of GSK-3 has been linked to various human diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative diseases.Two related isoforms of GSK-3 exist in mammals, GSK-3α and -β, which share a sequence identity within their catalytic domains of 98%.
Beyond the catalytic domains they show significant differences. Although these isoforms are structurally related, they are not functionally equivalent, and one cannot compensate for loss of the other.
The debate on the respective contributions of the isoforms GSK-3α and GSK-3β on the pathogenesis of different diseases is ongoing.
Various studies indicate that the therapies of certain diseases benefit from specific targeting of GSK-3α and GSK-3β. GSK-3α was recently identified as a differentiation target in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). AML is a hematopoietic malignancy defined by uncontrolled proliferation and disrupted myeloid differentiation. AML is the second most common form of leukemia in adults.
The current treatment of AML with conventional chemotherapy is very aggressive yet ineffective for the majority of patients with the disease.Thus, alternative targeted treatment approaches for AML are highly desirable. GSK-3α recently emerged as a potential target in this disease.
PAPER

The
challenge for glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) inhibitor design lies
in achieving high selectivity for one isoform over the other. The
therapy of certain diseases, such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML), may
require α-isoform specific targeting. The scorpion shaped GSK-3
inhibitors developed by our group achieved the highest GSK-3α
selectivity reported so far but suffered from insufficient aqueous
solubility. This work presents the solubility-driven optimization of our
isoform-selective inhibitors using a scorpion shaped lead. Among 15
novel compounds, compound 27 showed high activity against GSK-3α/β with the highest GSK-3α selectivity reported to date. Compound 27
was profiled for bioavailability and toxicity in a zebrafish embryo
phenotype assay. Selective GSK-3α targeting in AML cell lines was
achieved with compound 27, resulting in a strong differentiation
phenotype and colony formation impairment, confirming the potential of
GSK-3α inhibition in AML therapy
Evaluation of Improved Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3α Inhibitors in Models of Acute Myeloid Leukemia
† Clemens Schöpf Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry, Technische Universität Darmstadt, 64287 Darmstadt, Germany
‡ Department of Pediatric Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02215, United States
J. Med. Chem., Article ASAP
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01200
Publication Date (Web): October 23, 2015
Copyright © 2015 American Chemical Society
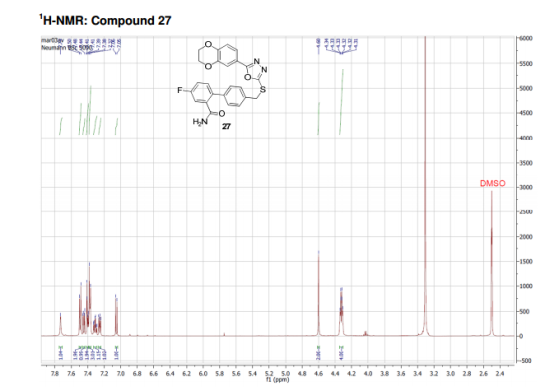
compound 27 as a colorless solid. HPLC: 96%, tR = 6.93 min.
1H NMR (DMSO-d6,
500 MHz, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 4.32 (td, J = 5.2 Hz, J = 3.7 Hz, 4H), 4.60
(s, 2H), 7.05 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.25 (dd, J = 9.1 Hz, J = 2.7 Hz,
1H), 7.31 (td, J = 8.6 Hz, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 7.38 (m, 3H), 7.41 (d, J =
2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.45 (dd, J = 8.4 Hz, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.2 Hz,
2H), 7.73 (s, 1H).
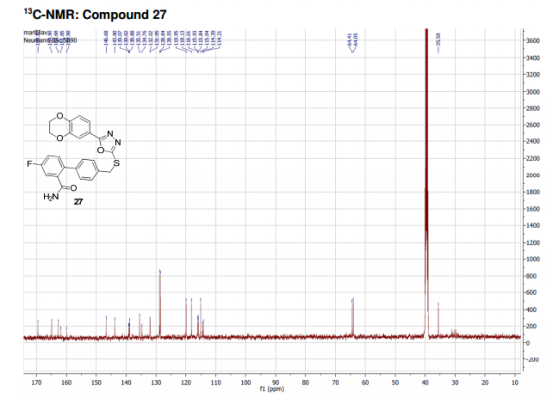
13C NMR (DMSO, 125 MHz, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 35.6, 64.1, 64.4, 114.3 (d, JC–F = 21 Hz), 115.0, 115.9 (d, JC–F = 21 Hz), 115.9, 118.1, 120.0, 128.6 (2C), 128.8 (2C), 132.0 (d, JC–F = 8 Hz), 134.8, 135.5, 138.9, 139.0 (d, JC–F = 7 Hz), 143.8, 146.7, 160.9 (d, JC–F = 247 Hz), 162.7, 164.9, 169.5.
EI-MS: m/z = 463 (100, [M+]), 464 (26, [M+ + H]), 465 (7, [M+ + 2H].
ABOUT Boris Schmidt
ABOUT Theresa Neumann
////////
































