Green Chem., 2018, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C7GC03325G, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/C7GC03325G, Paper
Evaldas Klumbys, Ziga Zebec, Nicholas J. Weise, Nicholas J. Turner, Nigel S. Scrutton
Cascade biocatalysis and metabolic engineering provide routes to cinnamyl alcohol.
Cascade biocatalysis and metabolic engineering provide routes to cinnamyl alcohol.
Bio-derived production of cinnamyl alcohol via a three step biocatalytic cascade and metabolic engineering
* Corresponding authors
Prof Nigel ScruttonScD, FRSC, FRSB
Professor of Enzymology and Biophysical Chemistry
Abstract
The construction of biocatalytic cascades for the production of chemical precursors is fast becoming one of the most efficient approaches to multi-step synthesis in modern chemistry. However, despite the use of low solvent systems and renewably resourced catalysts in reported examples, many cascades are still dependent on petrochemical starting materials, which as of yet cannot be accessed in a sustainable fashion. Herein, we report the production of the versatile chemical building block cinnamyl alcohol from the primary metabolite and the fermentation product L-phenylalanine. Through the combination of three biocatalyst classes (phenylalanine ammonia lyase, carboxylic acid reductase and alcohol dehydrogenase) the target compound could be obtained in high purity, demonstrable at the 100 mg scale and achieving 53% yield using ambient temperature and pressure in an aqueous solution. This system represents a synthetic strategy in which all components present at time zero are biogenic and thus minimises damage to the environment. Furthermore we extend this biocatalytic cascade by its inclusion in an L-phenylalanine overproducing strain of Escherichia coli. This metabolically engineered strain produces cinnamyl alcohol in mineral media using glycerol and glucose as the carbon sources. This study demonstrates the potential to establish green routes to the synthesis of cinnamyl alcohol from a waste stream such as glycerol derived, for example, from lipase treated biodiesel.
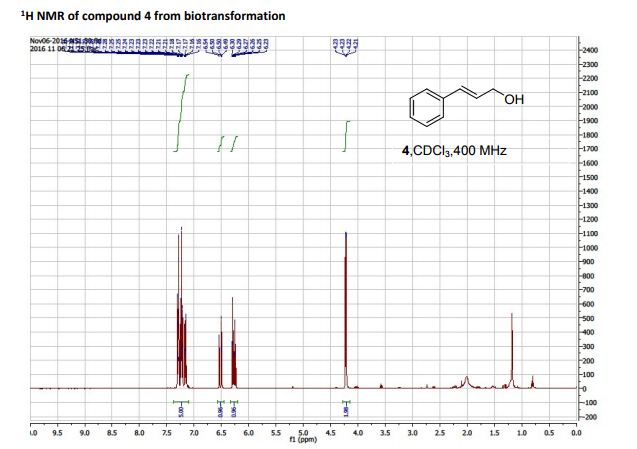
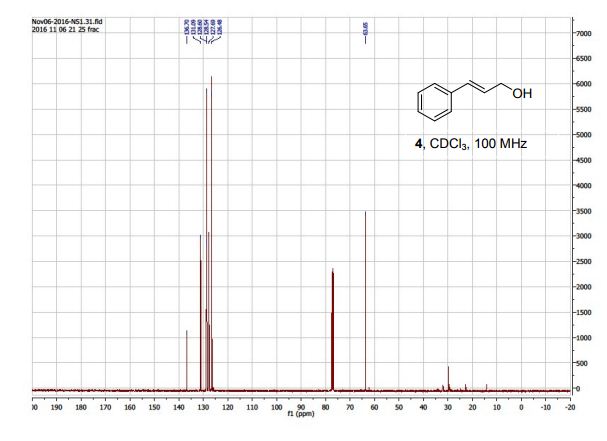
(R)-3-amino-3-(3-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid (1c) 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ 7.16-7.31 (m, 5H, ArH), 6.50-6.54 (d, 1H, J = 16 Hz, C=CH), 6.23-6.30 (dt, 1H, J = 16, 8 Hz, C=CHCH2 ), 4.21-4.23 (dd, 2H, J = 8, 4 Hz, C=CHCH2); 13C NMR (CDCl3): 136.70, 131.09, 128.60, 128.54, 127.69, 126.48, 63.65.


(R)-3-amino-3-(3-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid (1c) 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ 7.16-7.31 (m, 5H, ArH), 6.50-6.54 (d, 1H, J = 16 Hz, C=CH), 6.23-6.30 (dt, 1H, J = 16, 8 Hz, C=CHCH2 ), 4.21-4.23 (dd, 2H, J = 8, 4 Hz, C=CHCH2); 13C NMR (CDCl3): 136.70, 131.09, 128.60, 128.54, 127.69, 126.48, 63.65.
////////////cinnamyl alcohol, biocatalytic, metabolic engineering


Cinnamyl alcohol(CAS NO. 104-54-1) is an organic compound with very distinct sweet, spicy, hyacinth odour with the formula C6H5CH=CHCH2OH. Cinnamyl alcohol is also known by a variety of other names including cinnamic alcohol, 3-phenyl-2-propen-1-ol, 3-phenylprop-2-en-1-ol, zimtalcohol, styryl carbinol, e-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-ol, 3-phenylallyl alcohol, trans-cinnamyl alcohol.
ReplyDelete