C29H48N2O3S
Exact Mass: 504.33856
Saridegib also known as IPI-926 is an experimental drug
candidate undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of various types
of cancer, including hard to treat hematologic malignancies such as
myelofibrosis and ligand-dependant tumors such as chondrosarcoma.[1] IPI-926 exhibits its pharmacological effect by inhibition of the G protein-coupled receptor smoothened, a component of the hedgehog signaling pathway.[2] Chemically, it is a semi-synthetic derivative of the alkaloid cyclopamine. The process begins with cyclopamine extracted from harvested Veratrum californicum
which is taken through a series of alterations resulting in an analogue
of the natural product cyclopamine, making IPI-926 the only compound in
development/testing that is not fully synthetic.[2]
Saridegib is a member of a class of anti-cancer compounds known as hedgehog inhibitors (Hhi). Most of these compounds affect thehedgehog signaling pathway via inhibition of smoothened (Smo), a key component of the pathway. Depending on when a Hh inhibiting compound is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
(FDA), there may be a perceived need for one to be differentiated over
another for marketing purposes, which could lead to different
nomenclature (e.g., a Hhi or an agonist of Smo). This marketing
technique is more of a differentiation strategy than a scientific
property of these compounds, as the mechanism of action (MOA) in the end
is inhibition of the Hh pathway, targeting cancer stem cells. However,
as these new compounds are further studied, identification of
differences in a compound’s MOA, could lead to hypotheses regarding the
stage at which Smo is inhibited, where along the pathway the compound
binds, or specific binding properties of a compound. If these hypotheses
are proven, claims could be made regarding a specific compound’s MOA
and how it affects efficacy, safety, combinability with other cancer
treatments, etc. Scientific data in support of such hypotheses have not
been published to date.
There are currently no drugs in the Hhi class FDA approved, however IPI-926 and GDC-0449 are the 2 leading compounds in the class. IPI-926, GDC-0449, and LDE-225 are the only compounds that have generic names passed by the United States Adopted Name (USAN) council (Infinity IPI-926/saridegib, Genentech GDC-0449/vismodegib, and Novartis LDE-225/erismodegib). Although Infinity is further along in chondrosarcoma, myelofibrosis, and AML, Roche/Genentech recently submitted an NDA for GDC-0449 for the treatment of adults with advanced basal cell carcinoma (BCC) when surgery is no longer an option, and the FDA has accepted and has filed the NDA, giving it priority review status. Thus it appears that Roche/Genentech will be the first Hhi to market with GDC-0449, if approved, for the treatment of advanced BCC, with Infinity second to market with IPI-926 for treatment in chondrosarcoma. It appears Infinity will not pursue an indication for BCC and focus on cancers with high unmet needs.[1][3][4][5][6]
Other Hhi-class compounds not as far along in development as IPI-926 and GDC-0449 include:[7]

The hedgehog pathway inhibitor IPI-926 has been in clinical
investigation for basal cell carcinoma, chondrosarcoma, and pancreatic
cancer. In the final step of the synthesis of IPI-926 the drug
substance (DS) is isolated as the hydrochloride salt of the 2-propanol
(2-PrOH) solvateThere are currently no drugs in the Hhi class FDA approved, however IPI-926 and GDC-0449 are the 2 leading compounds in the class. IPI-926, GDC-0449, and LDE-225 are the only compounds that have generic names passed by the United States Adopted Name (USAN) council (Infinity IPI-926/saridegib, Genentech GDC-0449/vismodegib, and Novartis LDE-225/erismodegib). Although Infinity is further along in chondrosarcoma, myelofibrosis, and AML, Roche/Genentech recently submitted an NDA for GDC-0449 for the treatment of adults with advanced basal cell carcinoma (BCC) when surgery is no longer an option, and the FDA has accepted and has filed the NDA, giving it priority review status. Thus it appears that Roche/Genentech will be the first Hhi to market with GDC-0449, if approved, for the treatment of advanced BCC, with Infinity second to market with IPI-926 for treatment in chondrosarcoma. It appears Infinity will not pursue an indication for BCC and focus on cancers with high unmet needs.[1][3][4][5][6]
Other Hhi-class compounds not as far along in development as IPI-926 and GDC-0449 include:[7]
- Novartis’ LDE-225 (USAN generic name erismodegib)
- Exelixis/Bristol-Myers Squibb’s BMS-833923 (XL139)
- Millennium Pharmaceuticals’s TAK-441
- Pfizer’s PF-04449913
Fig 1. Chemical structure comparison between IPI-926 and cyclopamine
IPI-926 is currently developed by Infinity
Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Malignant activation of the Hedgehog pathway is
implicated in multiple cancer settings and Infinity’s development
strategy is designed to enable IPI-926 to target a broad range of
critical oncology targets – from the tumor cell to the cancer
microenvironment. This broadly applicable, targeted approach represents
an innovative method for fighting cancer and has potential in treating a
range of cancers, including pancreatic cancer, small cell lung cancer,
ovarian cancer, bladder cancer, medulloblastoma, basal cell carcinoma,
and certain hematological malignancies.
A design of experiments (DoE)
approach was taken to optimize purity and reaction yield of the final
debenzylation and hydrochloride salt formation of IPI-926. The study
involved a careful dissection of the different process steps to enable
an independent investigation of these steps while ensuring that process
streams were representative. The results enabled a streamlined process
from the final chemical transformation to the salting and isolation and
led to the elimination of variability in the process as well as a robust
control of impurities. The optimized process was applied to production
and demonstrated on the kilogram scale.
A Design of Experiments Approach to a Robust Final Deprotection and Reactive Crystallization of IPI-926, A Novel Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitor
Infinity Pharmaceuticals, 784 Memorial Drive, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139, United States
Org. Process Res. Dev., Article ASAP
DOI: 10.1021/acs.oprd.5b00214
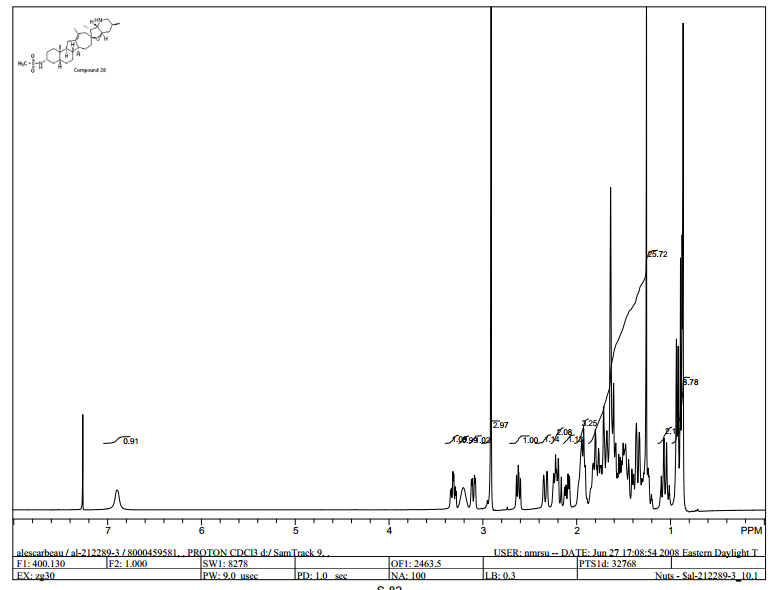
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) 6.90 (br s, 1H), 3.31 (dt, J = 10.6, 3.8 Hz, 1H), 3.20 (br s, 1H), 3.10 (dd, J = 13.7, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 2.91 (s, 3H), 2.62 (dd,J = 9.9, 7.6 Hz, 1H), 2.33 (br d, J = 14.5 Hz, 1H), 2.27–2.15 (m, 1H), 2.10 (dd, J = 14.5, 6.9 Hz, 1H), 1.99–1.17 (m, 28H), 1.05 (q, J = 11.6 Hz, 1H), 0.93 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H), 0.86 (s, 3H) ppm.
13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) 140.47, 124.53, 82.48, 76.97, 63.73, 54.08, 53.87, 50.12, 49.98, 47.19, 44.73, 42.27, 42.10, 40.24, 37.55, 37.44, 36.04, 34.44, 31.87, 31.33, 30.46, 29.79, 28.37, 27.94, 26.26, 24.19, 22.70, 18.92, 10.19 ppm;
MS: m/z = 505.29 [M + H]+.
………………………….
Tremblay, M. R.; Lescarbeau, A.; Grogan, M. J.; Tan, E.; Lin, G.; Austad, B. C.; Yu, L.-C.;Behnke, M. L.; Nair, S. J.; Hagel, M.; White, K.; Conley, J.; Manna, J. D.; Alvarez-Diez, T. M.; Hoyt, J.; Woodward, C. N.; Sydor, J. R.; Pink, M.; MacDougall, J.; Campbell, M. J.;Cushing, J.; Ferguson, J.; Curtis, M. S.; McGovern, K.; Read, M. A.; Palombella, V. J.;Adams, J.; Castro, A. C. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 4400– 4418, DOI: 10.1021/jm900305z
J. Med. Chem., 2009, 52 (14), pp 4400–4418
DOI: 10.1021/jm900305z
Recent evidence suggests that
blocking aberrant hedgehog pathway signaling may be a promising
therapeutic strategy for the treatment of several types of cancer.
Cyclopamine, a plant Veratrum alkaloid, is a natural product
antagonist of the hedgehog pathway. In a previous report, a
seven-membered D-ring semisynthetic analogue of cyclopamine, IPI-269609 (2),
was shown to have greater acid stability and better aqueous solubility
compared to cyclopamine. Further modifications of the A-ring system
generated three series of analogues with improved potency and/or
solubility. Lead compounds from each series were characterized in vitro
and evaluated in vivo for biological activity and pharmacokinetic
properties. These studies led to the discovery of IPI-926 (compound 28),
a novel semisynthetic cyclopamine analogue with substantially improved
pharmaceutical properties and potency and a favorable pharmacokinetic
profile relative to cyclopamine and compound2. As a result,
complete tumor regression was observed in a Hh-dependent medulloblastoma
allograft model after daily oral administration of 40 mg/kg of compound
28.
28 (4.06 g, 8.05 mmol, 95% for two steps). NMR δH (400 MHz, CDCl3) 6.90 (br s, 1H), 3.31 (dt, J = 10.6, 3.8 Hz, 1H), 3.20 (br s, 1H), 3.10 (dd, J = 13.7, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 2.91 (s, 3H), 2.62 (dd, J = 9.9, 7.6 Hz, 1H), 2.33 (br d, J = 14.5 Hz, 1H), 2.27−2.15 (m, 1H), 2.10 (dd, J = 14.5, 6.9 Hz, 1H), 1.99−1.17 (m, 28H), 1.05 (q, J = 11.6 Hz, 1H), 0.93 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H), 0.86 (s, 3H); NMR δC (100 MHz, CDCl3)
140.47, 124.53, 82.48, 76.97, 63.73, 54.08, 53.87, 50.12, 49.98, 47.19,
44.73, 42.27, 42.10, 40.24, 37.55, 37.44, 36.04, 34.44, 31.87, 31.33,
30.46, 29.79, 28.37, 27.94, 26.26, 24.19, 22.70, 18.92, 10.19; m/z = 505.29 [M + H]+; HPLC 99.1 a/a % at 215 nm.
Click on images for clear view……………..
References
- “Pipeline: IPI-926”. Infinity Pharmaceuticals.
- Tremblay, MR; Lescarbeau, A; Grogan, MJ; Tan, E; Lin, G; Austad, BC; Yu, LC; Behnke, ML et al. (2009). “Discovery of a potent and orally active hedgehog pathway antagonist (IPI-926)”. Journal of Medical Chemistry 52 (14): 4400–18. doi:10.1021/jm900305z. PMID 19522463.
- “Pipeline”. Infinity Pharmaceuticals.
- “Genentech Pipeline”. Genentech.
- “USAN Stem List” (PDF). AMA.
- “Names under consideration”. AMA.
- “Search results for Hh clinical trials”. United National Institute of Health’s ClinicalTrials.gov.
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-((2S,3R,3aS,3′R,4a′R,6S,6a′R,6b′S,7aR,12a&prmie;S,12b′S)-3,6,11′,12b′-tetramethyl-2′,3a,3′,4,4′,4a′,5,5&prmie;,6,6′,6a′,6b′,7,7a,7′,8′,10′,12′,12a′,12b′-icosahydro-1′H,3H-spiro[furo[3,2-b]pyridine-2,9′-naphtho[2,1-a]azulen]-3′-yl)methanesulfonamide
|
|
| Other names
saridegib
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| 1037210-93-7 |
|
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL538867 |
| ChemSpider | 26353073 |
| 8198 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 25027363 |
| UNII | JT96FPU35X |
| Properties | |
| C29H48N2O3S | |
| Molar mass | 504.77 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| Legal status |
|
/////Saridegib, IPI-926