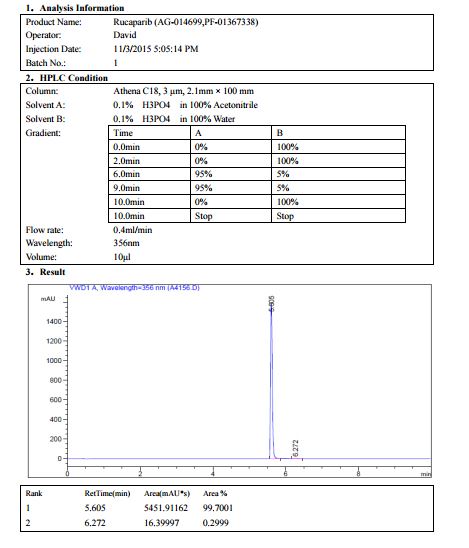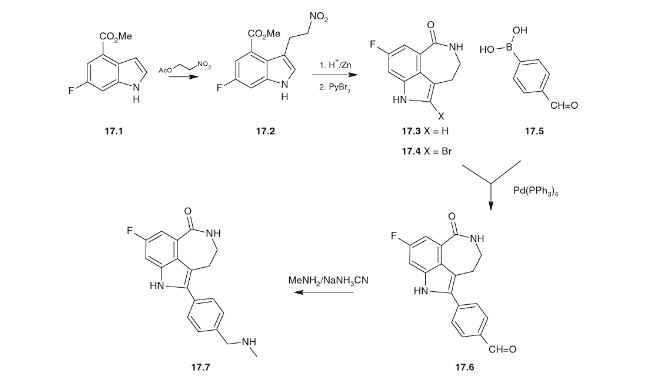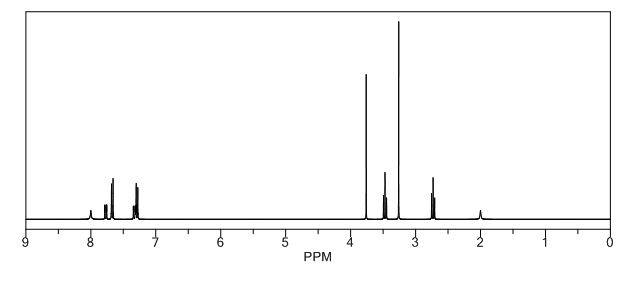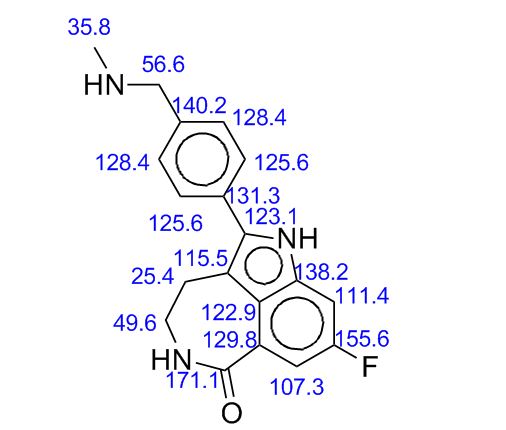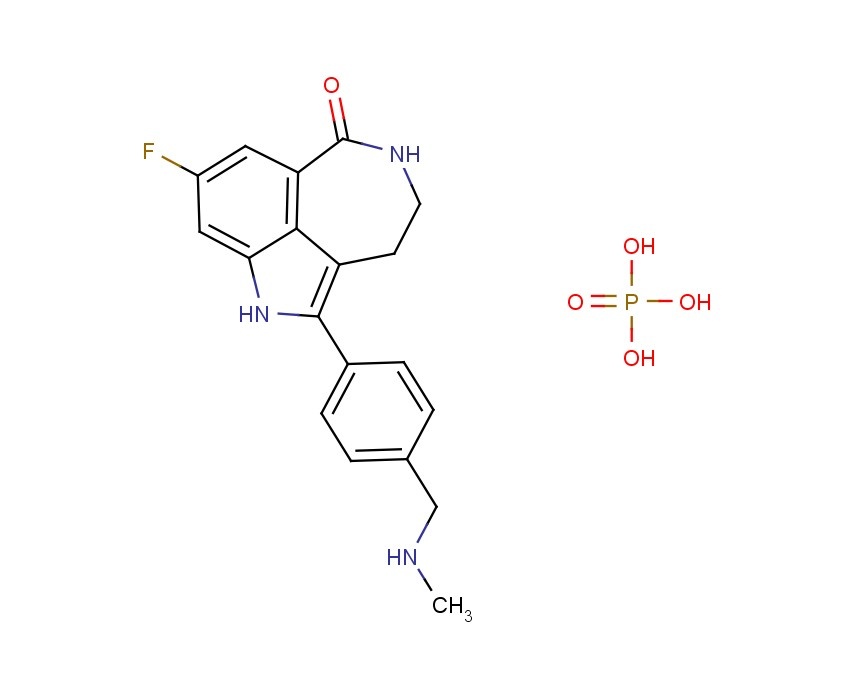
AG 014699, Rucaparib
AG014699, the phosphate salt of AG14447, which has improved aqueous solubility, has been selected for clinical trial.AG014699 is a tricyclic indole poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity.
M.Wt: 421.3593
Formula: C19H21FN3O5P
CAS No: 459868-92-9
SYN FROM BOOK
Examples of PARP-1 inhibitors
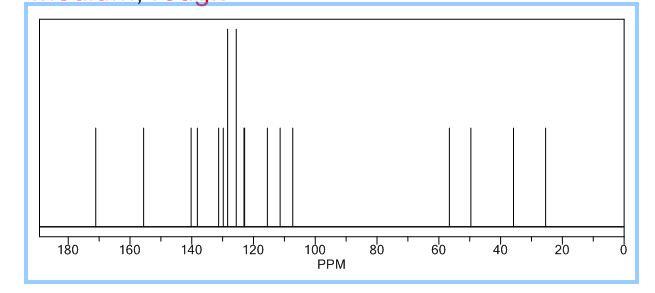
1H NMR PREDICT
13C NMR PREDICT

Rucaparib, PF-01367338283173-50-2 cas 6H-Pyrrolo[4,3,2-ef][2]benzazepin-6-one, 8-fluoro-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-2-[4-[(methylamino)methyl]phenyl]-6H- Azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one, 8-fluoro-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-2-[4-[(methylamino)methyl]phenyl] -8-Fluoro-2-[4-[(methylamino)methyl]phenyl]-1,3,4,5- tetrahydro-6H-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one;8-Fluoro-2-(4-methylaminomethyl-phenyl)-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one8-Fluoro-2-(4-methylaminomethyl-phenyI)-l,3,4,5-tetrahydro-azepino[5,4,3- cd]indol-6-one
- MW..C19 H18 F N3 O
- cas of csa salt-----1327258-57-0
- 773059-19-1 (hydrochloride)
773059-22-6 (L-tartrate)
773059-23-7 (acetate) - 459868-92-9 PHOSPHATE
- AG-014699
AG-14699
CO-338
PF-01367338
AG-014447 (free base)
AG-14447 (free base) - Agouron (Originator)
Pfizer (Originator) - Clovis Oncology
- WO 2014052550, WO 2014037313, WO 2000042040WO 2004087713WO 2005012305
Rucaparib (AG 014699) is a PARP inhibitor being investigated as a potential anti-cancer agent.
Rucaparib inhibits "the contraction of isolated vascular smooth muscle, including that from the tumours of cancer patients. It also reduces the migration of some cancer and normal cells in culture."[1]
It can be taken orally in tablet form.[2]
It has undergone phase I clinical trials for patients with advanced solid tumours.[3] It is in phase II clinical trials for metastatic breastand ovarian cancer with known BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation.[4][2]
It is thought that 20% of women with ovarian cancer who are not BRCA positive might also benefit from PARP inhibitors. Clinical trials are beginning (as of April, 2014)
As of November 2012 four clinical trials of rucaparib were recruiting patients.[5]
Inhibition of poly(ADP ribose) polymerase, or PARP, is an exciting new mechanism for the treatment of cancer.(1) The PARP enzyme is responsible for repair of damaged DNA in both normal and tumor cells, and inhibition of this repair mechanism is expected to make the cell more likely to undergo apoptosis. Preclinical work has shown that PARP inhibitors coadministered with a standard chemotherapuetic agent are more effective than the standard treatment aloneRucaparib is a NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase inhibitor in phase II clinical development at Cancer Research UK for the treatment of patients with advanced ovarian cancer and in patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Clovis Oncology is conducting early clinical evaluation of rucaparib for the treatment of triple negative breast cancer or ER/PR +, HER2 negative with known BRCA1/2 mutations p2 and for the treatment of gBRCA mutation breast cancer.. Pfizer discontinued development of rucaparibin 2011.In 2011, the compound was licensed to Clovis Oncology by Pfizer for the treatment of cancer. In 2012, orphan drug designation was assigned in the U.S. and the E.U. for the treatment of ovarian cancer.
Inhibition of poly(ADP ribose) polymerase, or PARP, is an exciting new mechanism for the treatment of cancer.(1) The PARP enzyme is responsible for repair of damaged DNA in both normal and tumor cells, and inhibition of this repair mechanism is expected to make the cell more likely to undergo apoptosis. Preclinical work has shown that PARP inhibitors coadministered with a standard chemotherapuetic agent are more effective than the standard treatment aloneRucaparib is a NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase inhibitor in phase II clinical development at Cancer Research UK for the treatment of patients with advanced ovarian cancer and in patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Clovis Oncology is conducting early clinical evaluation of rucaparib for the treatment of triple negative breast cancer or ER/PR +, HER2 negative with known BRCA1/2 mutations p2 and for the treatment of gBRCA mutation breast cancer.. Pfizer discontinued development of rucaparibin 2011.In 2011, the compound was licensed to Clovis Oncology by Pfizer for the treatment of cancer. In 2012, orphan drug designation was assigned in the U.S. and the E.U. for the treatment of ovarian cancer.
The compound 8-fluoro-2-{4-[(methylamino)methyl]phenyl}-1 ,3,4,5-tetrahydro-6H-azepino[5,4,3- cd]indol-6-one represented by formula
is a small molecule inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). 8-Fluoro-2-{4- [(methylamino)methyl]phenyl}-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-6H-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one and salts thereof, is disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 6,495,541 and PCT Application No. PCT/IB2004/000915, International Publication No. WO 2004/087713, the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference in their entireties. U.S. Provisional Patent Applications No. 60/612,459 and 60/679,296, entitled "Polymorphic Forms of the Phosphate Salt of 8-Fluoro-2-{4-[(methylamino)methyl]phenyl}-1 ,3,4,5-tetrahydro-6H- azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one," the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference in their entireties, describe novel polymorphic forms of the phosphate salt of 8-fluoro-2-{4- [(methylamino)methyl]phenyl}-1 ,3,4,5-tetrahydro-6H-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one, and methods for their preparation. U.S. Provisional Patent Applications No. 60/612,458; and 60/683,006, entitled "Therapeutic Combinations Comprising Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerases Inhibitor," the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference in its entirety, describe pharmaceutical combinations of 8-fluoro-2-{4- [(methylamino)methyl]phenyl}-1 ,3,4,5-tetrahydro-6H-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one.
PATENT
Example IIII:8-Fluoro-2-(4-methylaminomethyl-phenyI)-l,3,4,5-tetrahydro-azepino[5,4,3- cd]indol-6-one
4-(8-fluoro-6-oxo-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-lH-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-2-yl)- benzaldehyde (100 mg, 0.32 mmol; prepared in a manner similar to that described for compound 12 for 2-bromo-8-fluoro-l,3,4,5-tetrahydro-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one and 4-formylphenylboronic acid) was reacted with methylamine (1.62 mmol) as described for Compound PPP to yield 8-fluoro-2-(4-methylaminomethyl-phenyl)- l,3,4,5-tetrahydro-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one, 32 mg (31%) as a yellow solid: m.p. 1543-155 °C; Η NMR (300 MHz, d6-DMSO) 2.28 (s, 3H), 3.04 (m, 2H), 3.40 (m, 2H), 3.69 (s, 2H), 7.32 (dd, 7= 9.0, 2.4 Hz, IH), 7.44 (m, 3H), 7.57 (d, 7= 8.1 Hz, 2H), 8.25 (br t, IH), 11.67 (br s, IH). HRMS (MALDI MH+) Calcd for C19H18N3OF: 324,1512. Found: 325.1524. Anal. (C19H18N3OF03 H2O) C, H, N.
PAPER
Org. Process Res. Dev., 2012, 16 (12), pp 1897–1904
DOI: 10.1021/op200238p
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/op200238p Novel PARP inhibitor 1 is a promising new candidate for treatment of breast and ovarian cancer. A modified synthetic route to 1 has been developed and demonstrated on 7 kg scale. In order to scale up the synthesis to multikilogram scale, several synthetic challenges needed to be overcome. The key issues included significant thermal hazards present in a Leimgruber–Batcho indole synthesis, a low-yielding side-chain installation, a nonrobust Suzuki coupling and hydrogen cyanide generation during a reductive amination. In addition to these issues, changing from intravenous to oral delivery required a new salt form and therefore a new crystallization procedure. This contribution describes development work to solve these issues and scaling up of the new process in the pilot plant.
Novel PARP inhibitor 1 is a promising new candidate for treatment of breast and ovarian cancer. A modified synthetic route to 1 has been developed and demonstrated on 7 kg scale. In order to scale up the synthesis to multikilogram scale, several synthetic challenges needed to be overcome. The key issues included significant thermal hazards present in a Leimgruber–Batcho indole synthesis, a low-yielding side-chain installation, a nonrobust Suzuki coupling and hydrogen cyanide generation during a reductive amination. In addition to these issues, changing from intravenous to oral delivery required a new salt form and therefore a new crystallization procedure. This contribution describes development work to solve these issues and scaling up of the new process in the pilot plant.
 Novel PARP inhibitor 1 is a promising new candidate for treatment of breast and ovarian cancer. A modified synthetic route to 1 has been developed and demonstrated on 7 kg scale. In order to scale up the synthesis to multikilogram scale, several synthetic challenges needed to be overcome. The key issues included significant thermal hazards present in a Leimgruber–Batcho indole synthesis, a low-yielding side-chain installation, a nonrobust Suzuki coupling and hydrogen cyanide generation during a reductive amination. In addition to these issues, changing from intravenous to oral delivery required a new salt form and therefore a new crystallization procedure. This contribution describes development work to solve these issues and scaling up of the new process in the pilot plant.
Novel PARP inhibitor 1 is a promising new candidate for treatment of breast and ovarian cancer. A modified synthetic route to 1 has been developed and demonstrated on 7 kg scale. In order to scale up the synthesis to multikilogram scale, several synthetic challenges needed to be overcome. The key issues included significant thermal hazards present in a Leimgruber–Batcho indole synthesis, a low-yielding side-chain installation, a nonrobust Suzuki coupling and hydrogen cyanide generation during a reductive amination. In addition to these issues, changing from intravenous to oral delivery required a new salt form and therefore a new crystallization procedure. This contribution describes development work to solve these issues and scaling up of the new process in the pilot plant.
8-Fluoro-2-(4-methylaminomethyl-phenyl)-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one (1)
To a solution of aqueous sodium hydroxide (40% w/w, 3.6 kg, 2.0 equiv) in water (88 L, 14 L/kg) and methanol (35 L, 5.5 L/kg) was added 12 ............................................................deleted..........................and dried at 45 °C under vacuum to give 1 as a 1:1 THF solvate (5.57 kg, 14.08 mol, 84% yield);
mp (THF) dec at 220 °C;
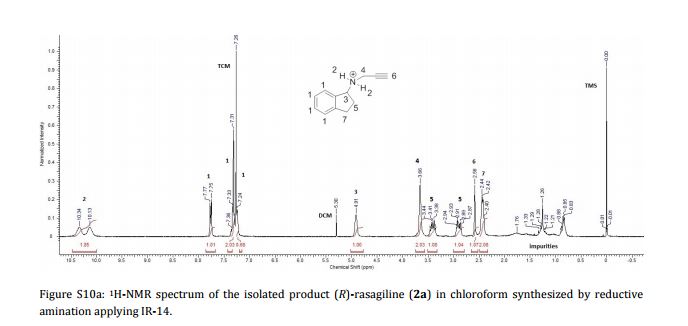
δH: (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) 2.25 (s, 3H), 2.99–3.01 (m 2H), 3.65 (s, 2H), 7.27 (dd, 1H, J = 2.4, 9.3 Hz), 7.39 (dd, 1H, J = 2.4, 9.3 Hz), 7.42 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 Hz), 7.53 (d, 2H, J = 8.3 Hz), 8.18 (t, br, 1H, J = 5.7 Hz), 11.60 (s, 1H);
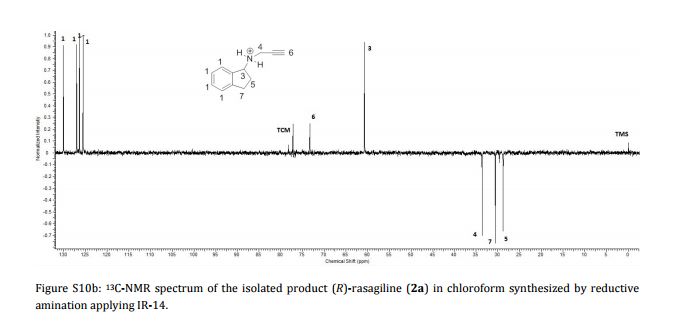
δC: (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) 28.74, 35.58, 41.84, 54.74, 100.47 (d, J = 25.8 Hz), 109.44 (d, J = 25.8 Hz), 111.47, 123.19, 125.72 (d, J = 8.8 Hz), 127.55, 128.20, 129.86, 135.38 (d, J = 3.7 Hz), 136.67 (d, J = 12.4 Hz), 140.52, 158.31 (d, J = 233), 168.39.
8-Fluoro-2-(4-methylaminomethyl-phenyl)-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one (S)-camphorsulfonate Salt (21)
To a slurry of 1 (5.32 kg, 13.48 mol) in isopropanol (30 L, 5.5 L/kg) and water (39 L, 7.3 L/kg) was added a solution of (S)-camphorsulfonic acid (3.75 kg, 16.18 mol, 1.2 equiv) in water (10.6 L, 2 L/kg). The resultant slurry was then heated to 70 °C and held for 1 h to ensure dissolution. ................................deleted.......................C to give 21 as a white crystalline solid (7.09 kg, 12.76 mol, 95% yield); mp (IPA/water) 303 °C;
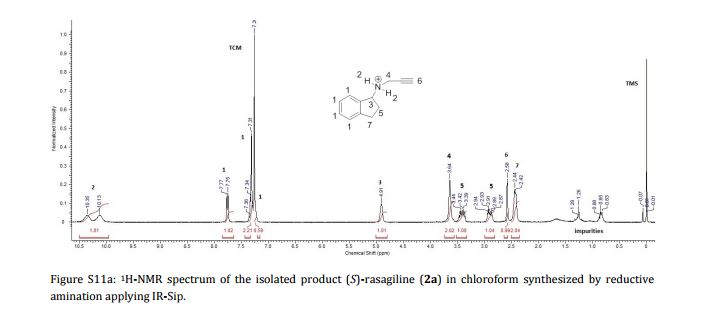
δH: (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) 0.74 (s, 3H), 1.05 (s, 3H), 1.28 (m, 1H), 1.80 (d, 1H, J = 18.0 Hz), 1.81–1.88 (m, 1H), 1.93 (app t, 1H, J = 4.5 Hz), 2.24 (m, 1H), 2.41 (d, 1H, J = 14.6 Hz), 2.62 (s, 3H), 2.66–2.72 (m, 1H), 2.91 (d, 1H, J = 14.7 Hz), 3.04–3.07 (m, br, 2H), 3.36–3.45 (m, br, 2H), 4.20 (s, 2H), 7.37 (dd, 1H, J = 2.4, 9.3 Hz), 7.44 (dd, 1H, J = 2.4, 11.0 Hz), 7.63 (d, 2H, J = 8.3 Hz), 7.71 (d, 2H, J = 8.3 Hz), 8.26 (t, br, 1H, J = 5.5 Hz), 11.76 (s, 1H);
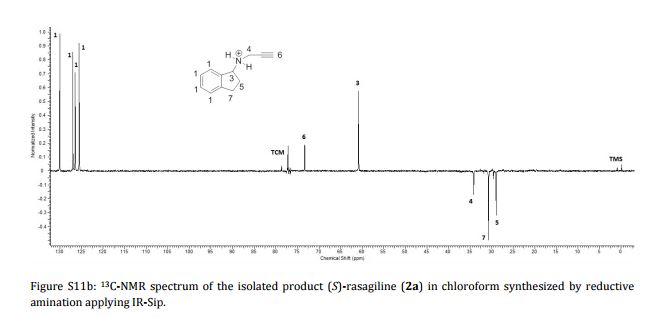
δC: (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) 19.51, 20.02, 24.14, 26.37, 28.74, 32.28, 41.77, 42.13, 42.22, 46.71, 47.00, 51.06, 58.21, 100.65 (d, J = 25.8 Hz), 109.72 (d, J = 25.8 Hz), 112.41, 123.03, 126.04 (d, J = 8.7 Hz), 127.98, 130.19, 131.22, 132.22, 134.50, 136.83 (d, J = 12.0 Hz), 158.52 (d, J = 235 Hz), 168.27, 216.24.
PATENT
WO 2006033003
The compound 8-fluoro-2-{4-[(methylamino)methyl]phenyl}-1 ,3,4,5-tetrahydro-6H-azepino[5,4,3- cd]indol-6-one represented by formula
is a small molecule inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). 8-Fluoro-2-{4- [(methylamino)methyl]phenyl}-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-6H-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one and salts thereof, is disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 6,495,541 and PCT Application No. PCT/IB2004/000915, International Publication No. WO 2004/087713, the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference in their entireties.
U.S. Provisional Patent Applications No. 60/612,459 and 60/679,296, entitled "Polymorphic Forms of the Phosphate Salt of 8-Fluoro-2-{4-[(methylamino)methyl]phenyl}-1 ,3,4,5-tetrahydro-6H- azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one," the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference in their entireties, describe novel polymorphic forms of the phosphate salt of 8-fluoro-2-{4- [(methylamino)methyl]phenyl}-1 ,3,4,5-tetrahydro-6H-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one, and methods for their preparation. U.S. Provisional Patent Applications No. 60/612,458; and 60/683,006, entitled "Therapeutic Combinations Comprising Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerases Inhibitor," the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference in its entirety, describe pharmaceutical combinations of 8-fluoro-2-{4- [(methylamino)methyl]phenyl}-1 ,3,4,5-tetrahydro-6H-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one.


Example 13. Synthesis of 8-Fluoro-2-(4-methylaminomethyl-phenyl)-1,3.4.5-tetrahvdro-azepinor5.4.3- ccflindol-6-one (15) i
- OriginatorClovis Oncology; Foundation Medicine
- ClassDiagnostic agents
Highest Development Phases
- RegisteredOvarian cancer
- Phase IIIFallopian tube cancer; Peritoneal cancer
- Clinical Phase UnknownCancer
Most Recent Events
- 19 Dec 2016Registered for Ovarian cancer (Diagnosis) in USA
- 23 Aug 2016Preregistration for Ovarian cancer (Diagnosis) in USA (unspecified route)
- 05 May 2016Clovis Oncology announces intention to submit PMA application to US FDA
CDxBRCA; FoundationFocus CDxBRCA; Rubraca companion diagnostic
Rucaparib phosphateis in phase Ⅲ clinical trials for the treatment of patients with advanced ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer and ovarian cancer. It was granted breakthrough therapy designation by FDA for the treatment of ovarian cancer in 2015.
The compound was originally developed by Pfizer, then licensed to Clovis Oncology by Pfizer in 2011 for the treatment of cancer.
SYN FROM BOOK
Examples of PARP-1 inhibitors
1H NMR PREDICT
13C NMR PREDICT
A CLIP

Original synthesis procedure and route (DOI: 10.1021/op200238p)

Optimized route
Initial route:
- 5-Fluoro-2-methylbenzoic acid (molbase): 550$/kg (84.78$/mol)
- Phthalimidoacetaldehyde diethyl acetal (molbase): 2369$/kg (623.73$/mol)
- 4-Formylphenylboronic acid (molbase) : 350 $/kg (52.48$/mol)
Total: 3269$/kg (760.99$/mol)
Optimized route:
- 4-Bromobenzaldehyde (molbase): 101$/kg (18.69$/mol)
- 5-Chlorovaleryl chloride (molbase): 141 $/kg (21.86$/mol)
- 3,5-Difluorobenzonitrile (molbase): 150 $/kg (20.87$/mol)
David Le Borgne
Process & R&D Chemist / C.Chem: Pharma & Micro-Electronic, Proces
https://davidleborgnechimie.blogspot.in/p/blog-page_6.html
Drug Name:Rucaparib PhosphateResearch Code:AG-014699; AG-14699; CO-338; PF-01367338Trade Name:MOA:Poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitorIndication:Ovarian cancer; Fallopian tube cancer; Peritoneum cancerStatus:Phase III (Active)Company:Pfizer (Originator) , Clovis Oncology
283173-50-2 (Rucaparib );
459868-92-9 (Rucaparib Phosphate)
459868-92-9 (Rucaparib Phosphate)
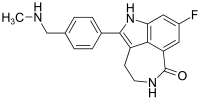 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
8-Fluoro-2-{4-[(methylamino)methyl]phenyl}-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-6H-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one
| |
Other names
AG014699
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Registry Number | 283173-50-2 |
| ChemSpider | 8107584 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| KEGG | D10079 |
| PubChem | 9931954 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C19H18FN3O |
| Molar mass | 323.37 g·mol−1 |
References
- http://www.qub.ac.uk/schools/SchoolofPharmacy/Filestore/Filetoupload,121186,en.pdf
- "Cancer Research launches new drug trial". 11 Jan 2011.
- "First in human phase I trial of the PARP inhibitor AG-014699 with temozolomide (TMZ) in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors".
- http://science.cancerresearchuk.org/research/loc/newcastle/newcastle_univ/plummerr/plummerrfr/plummerrfrp2/?version=1 URL no longer relevant
- Rucaparib trials
Clovis Oncology receives Breakthrough Therapy designation for rucaparib for treatment of advanced ovarian cancer in patients with BRCA-mutated tumours
7 April 2015 • Author: Victoria White
Clovis Oncology has announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted Breakthrough Therapy designation for the Company’s investigational agent rucaparib as monotherapy treatment of advanced ovarian cancer in patients who have received at least two lines of prior platinum-containing therapy, with BRCA-mutated tumours, inclusive of both germline BRCA (gBRCA) and somatic BRCA (sBRCA) mutations.
http://www.europeanpharmaceuticalreview.com/30569/news/industry-news/clovis-oncology-receives-breakthrough-therapy-designation-for-rucaparib-for-treatment-of-advanced-ovarian-cancer-in-patients-with-brca-mutated-tumours/
2525 28th Street
Suite 100
Boulder, CO 80301
Tel: 303.625.5000
Fax: 303.245.0360
Suite 100
Boulder, CO 80301
Tel: 303.625.5000
Fax: 303.245.0360

are a biopharmaceutical company focused on acquiring, developing and commercializing cancer treatments in the United States, Europe and other international markets. Our development programs are targeted at specific subsets of cancer, combining personalized medicine with companion diagnostics to direct therapeutics to those patients most likely to benefit from them.
We have three product candidates in clinical development: rociletinib (CO-1686), which is in Phase II development for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer; rucaparib, which is in Phase II and Phase III clinical trials for the treatment of ovarian cancer; and lucitanib, which is in Phase II clinical trials for the treatment of breast and lung cancers. We have received Breakthrough Therapy designation from the FDA for rociletinib and rucaparib. We maintain global rights for rociletinib and rucaparib, and U.S. and Japanese rights to lucitanib.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today granted accelerated approval to Rubraca (rucaparib) to treat women with a certain type of ovarian cancer. Rubraca is approved for women with advanced ovarian cancer who have been treated with two or more chemotherapies and whose tumors have a specific gene mutation (deleterious BRCA) as identified by an FDA-approved companion diagnostic test.
For Immediate Release
December 19, 2016
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today granted accelerated approval to Rubraca (rucaparib) to treat women with a certain type of ovarian cancer. Rubraca is approved for women with advanced ovarian cancer who have been treated with two or more chemotherapies and whose tumors have a specific gene mutation (deleterious BRCA) as identified by an FDA-approved companion diagnostic test.
“Today’s approval is another example of the trend we are seeing in developing targeted agents to treat cancers caused by specific mutations in a patient’s genes,” said Richard Pazdur, M.D., director of the Office of Hematology and Oncology Products in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research and acting director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence. “Women with these gene abnormalities who have tried at least two chemotherapy treatments for their ovarian cancer now have an additional treatment option.”
The National Cancer Institute estimates that 22,280 women will be diagnosed with ovarian cancer in 2016 and an estimated 14,240 will die of this disease. Approximately 15 to 20 percent of patients with ovarian cancer have a BRCA gene mutation.
BRCA genes are involved with repairing damaged DNA and normally work to prevent tumor development. However, mutations of these genes may lead to certain cancers, including ovarian cancers. Rubraca is a poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitor that blocks an enzyme involved in repairing damaged DNA. By blocking this enzyme, DNA inside the cancerous cells with damaged BRCA genes may be less likely to be repaired, leading to cell death and possibly a slow-down or stoppage of tumor growth.
Today, the FDA also approved the FoundationFocus CDxBRCA companion diagnostic for use with Rubraca, which is the first next-generation-sequencing (NGS)-based companion diagnostic approved by the agency. The NGS test detects the presence of deleterious BRCA gene mutations in the tumor tissue of ovarian cancer patients. If one or more of the mutations are detected, the patient may be eligible for treatment with Rubraca.
The safety and efficacy of Rubraca were studied in two, single-arm clinical trials involving 106 participants with BRCA-mutated advanced ovarian cancer who had been treated with two or more chemotherapy regimens. BRCA gene mutations were confirmed in 96 percent of tested trial participants with available tumor tissue using the FoundationFocus CDxBRCA companion diagnostic. The trials measured the percentage of participants who experienced complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors (overall response rate). Fifty-four percent of the participants who received Rubraca in the trials experienced complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors lasting a median of 9.2 months.
Common side effects of Rubraca include nausea, fatigue, vomiting, low levels of red blood cells (anemia), abdominal pain, unusual taste sensation (dysgeusia), constipation, decreased appetite, diarrhea, low levels of blood platelets (thrombocytopenia) and trouble breathing (dyspnea). Rubraca is associated with serious risks, such as bone marrow problems (myelodysplastic syndrome), a type of cancer of the blood called acute myeloid leukemia and fetal harm.
The agency approved Rubraca under its accelerated approval program, which allows approval of a drug to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition based on clinical data showing the drug has an effect on a surrogate (substitute) endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit. The sponsor is continuing to study this drug in patients with advanced ovarian cancer who have BRCA gene mutations and in patients with other types of ovarian cancer. The FDA also granted the Rubraca application breakthrough therapy designation and priority review status. Rubraca also received orphan drug designation, which provides incentives such as tax credits, user fee waivers and eligibility for exclusivity to assist and encourage the development of drugs intended to treat rare diseases.
Rubraca is marketed by Clovis Oncology, Inc. based in Boulder, Colorado. The FoundationFocus CDxBRCA companion diagnostic is marketed by Foundation Medicine, Inc. of Cambridge, Massachusetts.
P.S. : The views expressed are my personal and in no-way suggest the views of the professional body or the company that I represent.
///////////
CNCc1ccc(cc1)-c1[nH]c2cc(F)cc3C(=O)NCCc1c23
Boulder, Colorado
Boulder, Colorado - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boulder,_ColoradoLocation in Boulder County and the State of Colorado. Coordinates: ... ZIP codes,80301-80310, 80314, 80321-80323, 80328, 80329. Area code(s), Both 303 ...

View of Boulder from Bear Peak





P.S. : The views expressed are my personal and in no-way suggest the views of the professional body or the company that I represent.
///////