Dear blog reader , this post is for brushing up our fundamentals of spectroscopy using simple molecules like aspirin
text may be less but graphs are educative. one can browse through this to brush up
 Product Name: Acetylsalicylic acid
CAS:50-78-2
Product Name: Acetylsalicylic acid
CAS:50-78-2



1H NMR

Assign. Shift(ppm)
A 11.
B 8.125
C 7.624
D 7.356
E 7.142
F 2.352
ABOVE IS PROTON NMR OF ASPIRIN AND ITS INTERPRETATION
abelled.
The peaks I have are:
- 2.30ppm (I this is a singlet and would be F)
- 7.07ppm (I think this is E)
- 7.29ppm (I think this is D)
- 7.53ppm (I think this is C)
- 8.05ppm (I think this is B)
- 11.44ppm (this is a singlet and would be A)
For B,C,D,E I need to say what kind of splitting pattern there would be and how many coupling constants are present and there approximate value. I think I know the assignments of them but I don't know the splitting pattern or coupling constants.
Would E and B be doublet of doublets because they couple with D and C so they would have ortho and meta coupling?
Would D and C be coupling with each other and B and E so would they be doublet of doublets of doublets, with two ortho and one meta coupling?



 DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO .....FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO .....FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
Join me on Linkedin

Join me on Facebook
 FACEBOOK
FACEBOOK
Join me on twitter

 amcrasto@gmail.com
amcrasto@gmail.com
BELOW IS IR OF ASPIRIN KBR DISC


IR in nujol mull

....................................................................................................................................................................

MASS SPECTRUM
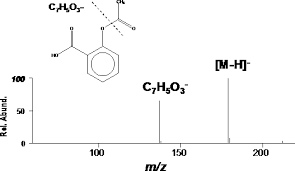

above is mass spectrum of aspirin
o-acetoxybenzoic acid
C9H8O4 (Mass of molecular ion: 180)
Source Temperature: 170 °C
Sample Temperature: 100 °C
DIRECT, 75 eV

13 C NMR

above is 13 C NMR OF ASPIRIN
| 50.18 MHz |
| C9 H8 O4
|
0.039 g : 0.5 ml CDCl3 |
ppm Int. Assign.
170.20 450 1
169.76 510 2
151.28 560 3
134.90 924 4
132.51 1000 5
126.17 986 6
124.01 974 7
122.26 397 8
20.99 674 9
=================================================

below is Raman spectra of aspirin

NMR INTERPRETATIONS
H-NMR spectral analysis

CAS NO. 50-78-2, Acetylsalicylic acid H-NMR spectral analysis
|
C-NMR spectral analysis

CAS NO. 50-78-2, Acetylsalicylic acid C-NMR spectral analysis
H, H-COSY spectrum
In H, H-COSY spectrum are on both axes, the 1 H chemical shifts plotted; In principle, both the axes 1 to see H-NMR spectra. Thus, there is a symmetric to the diagonal diagram.
1 H-NMR spectrum of acetylsalicylic acid
H, H-COSY spectrum of acetylsalicylic acid
In the spectrum, only the range from 7.0 to 8.2 ppm is applied, because only here HH scalar couplings can be expected.
There are two types of signals:
- Diagonal signals: join the coordinates δ a δ a (in core A), δ b δ b (in core B) ... on, but play no role in the evaluation of the couplings between different cores, since it is only the signal of a nucleus is. The diagonal with all its signals corresponding to the 1D H-NMR spectrum.
- EXAMPLE
Acetylsalicylic acid
7.13 ppm / 7.13 ppm = δ 2 δ 2 (H atom 2)
7.34 ppm / 7.34 ppm = δ 4 δ 4 (H atom 4)
7.61 ppm / 7.61 ppm = δ 3 δ 3 (H atom 3)
8.11 ppm / 8.11 ppm = δ 5 δ 5 (H atom 5)
- Cross signals: These signals are based on the scalar spin-spin coupling and are suitable for the evaluation of spectra of enormous importance.
- EXAMPLE
Acetylsalicylic acid
7.13 ppm / 7.61 ppm (δ 2 δ 3 ), and 7.61 ppm / 7.13 ppm (δ 3 δ 2 ) - vicinal coupling between the H-atoms 2 and 3
7.34 ppm / 7.61 ppm (δ 4 δ 3 ) and 7.61 ppm / 7.34 ppm (δ 3 δ 4 ) - vicinal coupling between the H-atoms 4 and 3
7.34 ppm / 8.11 ppm (δ 4 δ 5 ) and 8.11 ppm / 7.34 ppm (δ 5 δ 4 ) - vicinal coupling between the H-atoms 4 and 5
In general it can be seen in the COSY spectrum each scalar coupling between two nuclei at four signals (two cross and two diagonal peaks) resulting connected a square; in the following example, the vicinal coupling between the H atoms is highlighted 3 and 4.
With good resolution of the COSY spectrum, the coupling constants can be determined from the fine structure of the cross and diagonal signals, but this is rarely done because of the 1-D H-NMR spectra is easily possible.
 DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO .....FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO .....FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
Join me on Linkedin

Join me on Facebook  FACEBOOK FACEBOOK
Join me on twitter 
 amcrasto@gmail.com amcrasto@gmail.com

Location of Khajuraho Group of Monuments in India.
 Location in Madhya Pradesh Location in Madhya Pradesh
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Khajuraho_Group_of_Monuments
The Khajuraho Group of Monuments are a group of Hindu and Jain temples in Madhya Pradesh, India. About 620 kilometres (385 mi) southeast of New Delhi, ...
Hotel Chandela - A Taj Leisure Hotel
|