
ELETRIPTAN
Eletriptan, UK-116044-04(HBr salt), UK-116044, Relpax
143322-58-1 CAS OF FREE BASE
143577-61-1 (hemisuccinate), 179041-30-6 (monofumarate), 177834-92-3 (monoHBr salt), 180637-87-0 (monosuccinate)
| (R)-3-[(-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-5-(2-phenylsulfonylethyl)- 1H-indole |
Eletriptan hydrobromide was first disclosed in U.S. patent 5,545,644 (1996), assigned to Pfizer, New York, claiming the product “eletriptan” and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. ].
However, a detailed study on the profile of the impurities present and their synthesis has not yet been cited anywhere, except for in the case of some metabolites . Eletriptan hydrobromide is a second-generation drug serotonin (5-HT1) agonist used in the management of sensations of tightness, pain, pressure and heaviness in the precordium, throat and jaws.
Eletriptan is more lipophilic than other triptans and absorbed more quickly than sumatriptan in the intestinal absorption. Eletriptan is more effective than sumatriptan in reducing the blood vessels surrounding the brain, which cause the swelling that is associated with the headache pain of a migraine attack, by blocking the release of substances from the nerve endings that causes more pain.
1H NMR PREDICT
....................
13C NMR

.............
13C NMR
.............

5-Bromoindole under Heck reaction conditions is coupled with phenyl vinyl sulfone followed by acylation with Cbz-Proline acid chloride to obtain a compound of Formula IV which on reduction in presence of a hydride agent provide Eletriptan.
1H NMR CDCI3 δ= 8.10 (bs, NH), 7.92-7.99 5 (m, 2H), 7.62-7.69 (m, 1H), 7.53-7.61 (m, 2H), 7.30 (s, 1H), 7.22 (d, 1H), 7.03 (s, 1H), 6.93 (dd, 1 H), 3.38-3.45 (m, 2H), 3.09-3.21 (m, 4H), 2.45-2.55 (m, 2H), 2.45 (s, 3H), 2.20-2.30 (m, 1H), 1.50-1.90 (m, 4H).
ESI Mass (M+H) 383.69
...........
An overview of the key routes to the best selling 5-membered ring heterocyclic pharmaceuticals
Marcus Baumann, Ian R. Baxendale, Steven V. Ley and Nikzad Nikbin
Innovative Technology Centre, Department of Chemistry, University of Cambridge, Lensfield Road, CB2 1EW Cambridge, UK
Editor-in-Chief: J. Clayden
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2011, 7, 442–495.
Eletriptan (87, Relpax) is yet another indole-containing antimigraine drug. A process route for the synthesis of eletriptan published by Pfizer starts from a preformed bromo-indole 88 [28] (Scheme 20). In order to perform the acylation of the indole ring on larger scale, ethylmagnesium bromide and the corresponding acid chloride 89 are added concurrently from two different sides of the reactor to stop these reagents reacting with each other. This method of adding the reagents circumvents the necessity to isolate the magnesium salt of the indole and increases the yield from 50 to 82%. The carbonyl group of the proline side chain is then reduced simultaneously with the complete reduction of the Cbz-group to a methyl group with lithium aluminium hydride. Finally, the sulfonate side chain is introduced via a Heck-type coupling similar to that of naratriptan (Scheme 15), followed by hydrogenation of the double bond to afford eletriptan (Scheme 20).
![[1860-5397-7-57-i20]](http://beilstein-journals.org/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-7-57-i20.png?max-width=550&background=FFFFFF)
A rather ingenious Mitsunobu coupling reaction has been used to create a highly functionalised substrate 96 for an intramolecular Heck reaction resulting in a very short and succinct synthesis of eletriptan and related analogues 97 [29] (Scheme 21).
![[1860-5397-7-57-i21]](http://beilstein-journals.org/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-7-57-i21.png?max-width=550&background=FFFFFF)
Scheme 21: Heck coupling for the indole system in eletriptan.
Interestingly, it was found that the most obvious approach, the direct Fischer indole synthesis, to prepare the core of eletriptan as shown in Scheme 22 is not successful [30]. This is believed to be due to the instability of the phenyl hydrazine species 98 under the relatively harsh reaction conditions required to promote the cyclisation.
![[1860-5397-7-57-i22]](http://beilstein-journals.org/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-7-57-i22.png?max-width=550&background=FFFFFF)
Scheme 22: Attempted Fischer indole synthesis of elatriptan.
However, this problem could be avoided by using an acid-labile oxalate protected hydrazine 104 as depicted in Scheme 23. The yield of this step can be further improved up to 84% if the corresponding calcium oxalate is used.
![[1860-5397-7-57-i23]](http://beilstein-journals.org/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-7-57-i23.png?max-width=550&background=FFFFFF)
Scheme 23: Successful Fischer indole synthesis for eletriptan.
- Macor, J. E.; Wythes, M. J. Indole Derivatives. U.S. Patent 5,545,644, Aug 13, 1996.
- Perkins, J. F. Process for the Preparation of 3-Acylindoles. Eur. Patent 1088817A2, April 4, 2001.
- Ashcroft, C. P. Modified Fischer Indole Synthesis for Eletriptan. WO Patent 2005/103035, Nov 3, 2005.
- Bischler, A. Chem. Ber. 1892, 25, 2860–2879. doi:10.1002/cber.189202502123
............
.................
Synthesis of compounds related to the anti-migraine drug eletriptan hydrobromide
Suri Babu Madasu1,2, Nagaji Ambabhai Vekariya1, M. N. V. D. Hari Kiran1, Badarinadh Gupta1, Aminul Islam1, Paul S. Douglas2 and Korupolu Raghu Babu2
1Chemical Research and Development, Aurobindo Pharma Ltd., Survey No. 71 & 72, Indrakaran (V), Sangareddy (M), Medak Dist-502329, Andhra Pradesh, India
2Engineering Chemistry Department, AU College of Engineering, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam-530003, Andhra Pradesh, India
2Engineering Chemistry Department, AU College of Engineering, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam-530003, Andhra Pradesh, India
Associate Editor: J. Aube
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 1400–1405.
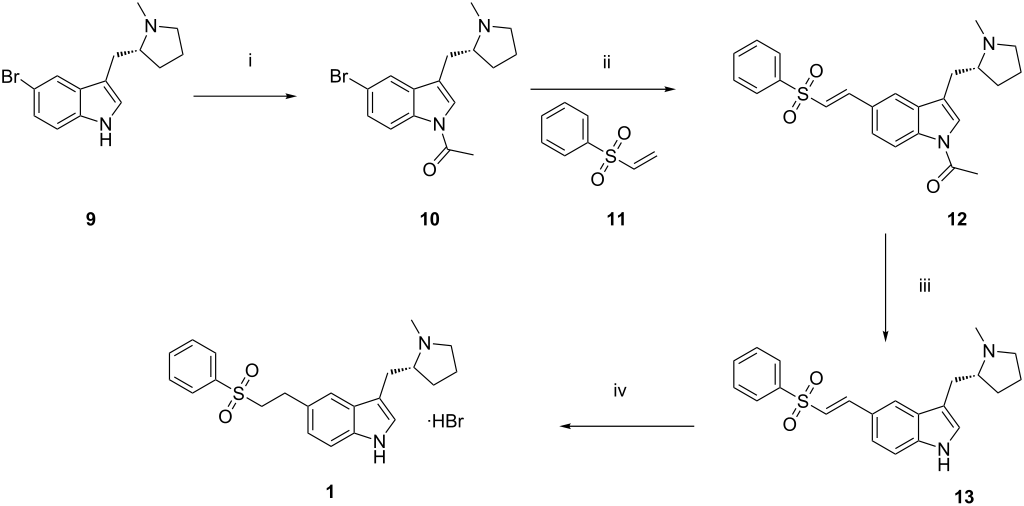
Synthetic route of eletriptan hydrobromide. Reagents and conditions: (i) Acetic anhydride, TEA, DMF, 90–100 °C; (ii) palladium acetate, tri-(o-tolyl)phosphine, TEA, DMF, 90–100 °C; (iii) methanol, K2CO3, acetonitrile, H2O, 5–10 °C; (iv) palladium on carbon, acetone, H2O, aqueous hydrobromic acid, IPA, 25–30 °C.
.............
Org. Process Res. Dev., 2011, 15 (1), pp 98–103
DOI: 10.1021/op100251q
aReagents and conditions: (a) EtMgBr, Et2O. (b) 3, DCM, 50% from 1. (c) LiAlH4, THF, 72%. (d) Ac2O, TEA, DMF. (e) Phenyl vinyl sulfone (PVS), Pd(OAc)2, P(°Tol)3, TEA, DMF, 80% from 5. (f) H2, Pd/C, MeSO3H, acetone, 95%. (g) K2CO3, MeOH, 92%. (h) HBr, acetone 73%.
1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 1.51−1.85 (m, 4H), 2.22−2.28 (m, 1H), 2.43−2.49 (m, 4H), 2.56−2.62 (m, 1H), 3.11−3.18 (m, 4H), 3.42−3.46 (m, 2H), 6.91−6.93 (s, 1H), 7.01 (s, 1H), 7.23−7.27 (d, 1H), 7.31 (s, 1H), 7.56−7.60 (m, 2H), 7.65−7.68 (m, 1H), 7.96−7.98 (d, 2H), 8.14 (s, 1H); LC/MS: Rt = 2.30 min; m/z 383 [MH]+
..............................
ELETRIPTAN HYDROBROMIDE MONOHYDRATE
'H-NMR (400MHz, ds-DMSO): delta = 10.90 (1H, d, J=2.2Hz), 9.35 (1 H, br s), 7.95 (2H, d, J=7.5Hz), 7.76 (1 H, t, J=7.5Hz), 7.66 (2H, t, J=7.5Hz), 7.38 (1 H, s), 7.24 (1 H, d, J=8.3Hz), 7.23 (1 H, d, J=2.2Hz), 6.92 (1 H, dd, J=8.3,1.4Hz), 3.63 (2H, m), 3.58 (2H, br m), 3.24 (1 H, m), 3.06 (1 H, m), 2.95 (2H, m), 2.86 (1 H, m), 2.83 (3H, s), 2.00 (1 H, m), 1.90 (2H, m), 1.70 (1 H, m).
Found: C, 54.85; H, 6.03; N, 5.76. C22H29N203SBr requires C, 54.87; H, 6.08; N, 5.82%.
1H NMR
13C PREDICT
COSYPREDICT
SYNTHESIS
US2012/71669 A1, ;
US2011/166364 A1, ;
WO2011/4391 A2, ;
WO2012/4811 A1, ;
US2008/287519 A1, ; Page/Page column 10 ;
WO2011/4391 A2, ; Page/Page column 19 ;
US2008/287519 A1, ; Page/Page column 8 ;
1H NMR
13C PREDICT
COSYPREDICT
SYNTHESIS
Reference:
KANSAL, Vinod Kumar; MISTRY, Dhirenkumar N.; PATEL, Rakesh Ravjibhai; PANDEY, Saurabh Patent: US2009/299077 A1, 2009 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 8 ;
USV Limited B.S.D. Mar Patent: US2012/71669 A1, 2012 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 11 ;
US2011/166364 A1, ;
WO2011/4391 A2, ;
WO2012/4811 A1, ;
US2008/287519 A1, ; Page/Page column 10 ;
WO2011/4391 A2, ; Page/Page column 19 ;
US2008/287519 A1, ; Page/Page column 8 ;




No comments:
Post a Comment