3-Phenylpropionic acid (2z) 1
1) Jiang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8344
Yield: 94% (142 mg), white solid. Melting point: 47-49 °C (lit.18 49 °C)
(18) Helavi, V. B.; Solabannavar, S. B.; Desai, U. V.; Mane, R. B. J. Chem. Research 2003, 3, 174.
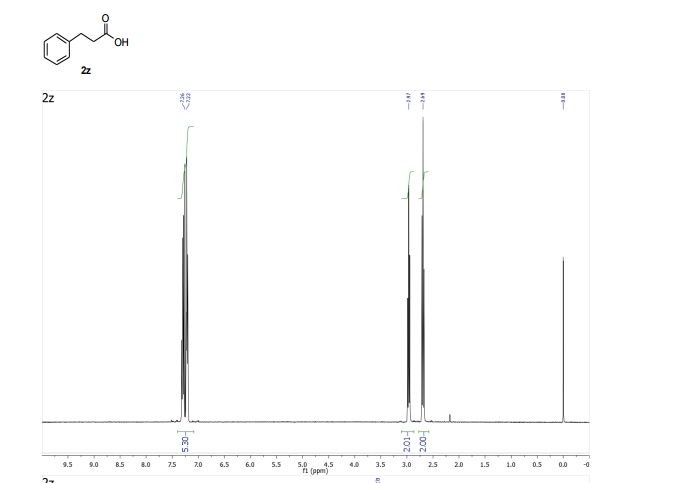
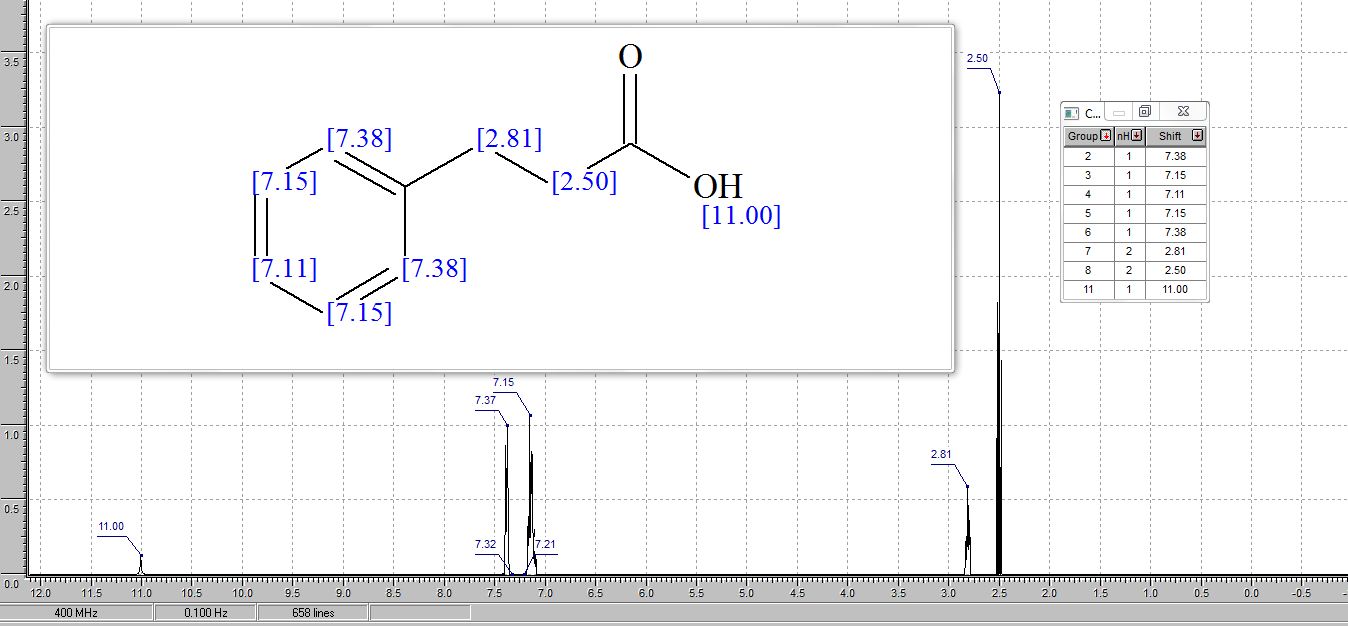
1 H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.34 – 7.17 (m, 5H), 2.97 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 2.69 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H).
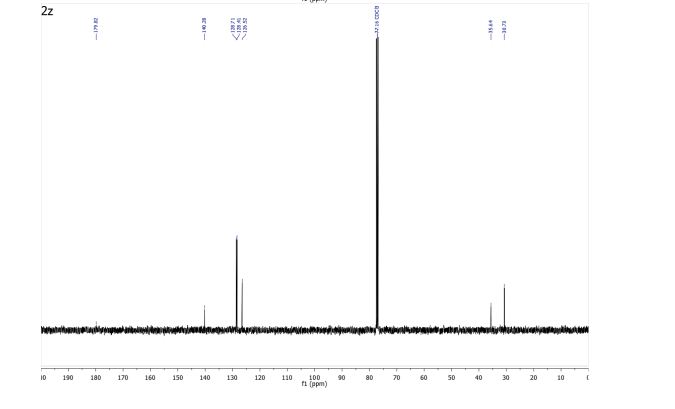
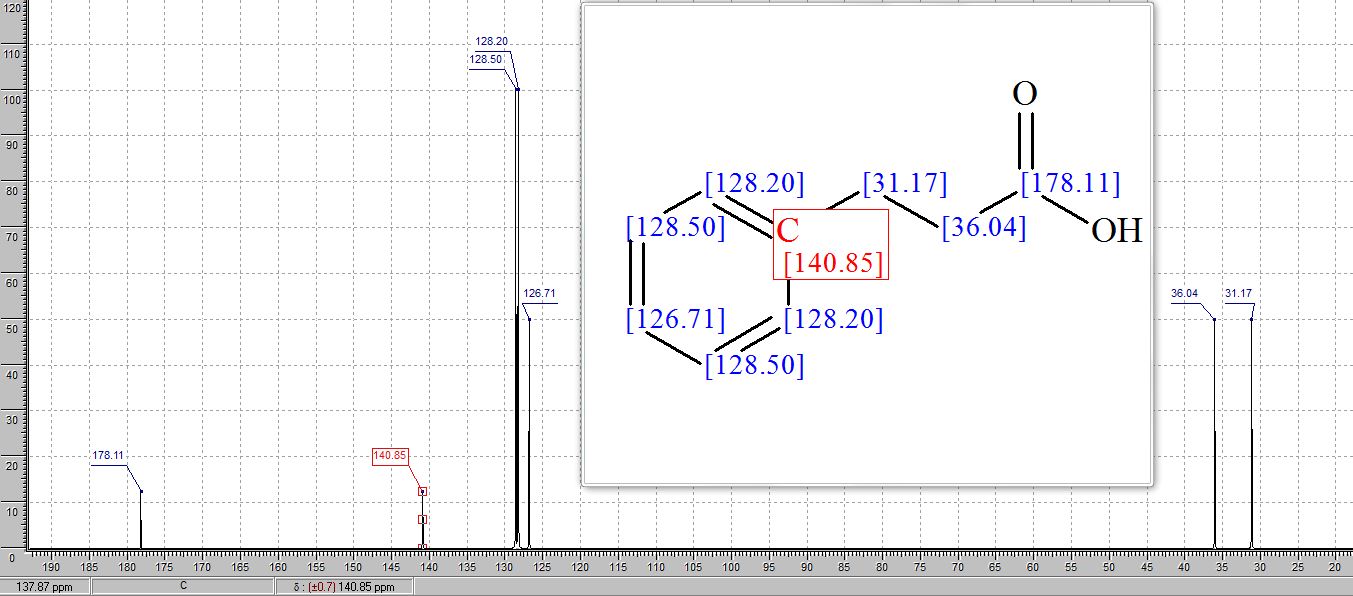
13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 179.82, 140.28, 128.71, 128.41, 126.52, 35.64, 30.73
1H AND 13C NMR PREDICT
Aerobic Oxidation of Diverse Primary Alcohols to Carboxylic Acids with a Heterogeneous Pd–Bi–Te/C (PBT/C) Catalyst
†Department of Chemistry and ‡Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wisconsin 53706, United States
Org. Process Res. Dev., Article ASAP
DOI: 10.1021/acs.oprd.7b00223
*E-mail: stahl@chem.wisc.edu.

Maaz Ahmed
PhD Candidate in the Stahl Lab at University of Wisconsin-Madison

Prof. Shannon S. Stahl
Department of Chemistry
University of Wisconsin-Madison
1101 University Avenue
Madison , Wisconsin 53706
Tel: (608) 265-6288
Fax: (608) 262-6143
stahl@chem.wisc.edu
Room 6132a Chemistry
University of Wisconsin-Madison
1101 University Avenue
Madison , Wisconsin 53706
Tel: (608) 265-6288
Fax: (608) 262-6143
stahl@chem.wisc.edu
Room 6132a Chemistry
Abstract

Heterogeneous catalytic aerobic oxidation methods represent a near-ideal approach for the conversion of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids. Here, we report that a heterogeneous catalyst composed of Pd, Bi, and Te supported on activated carbon is highly effective for the oxidation of diverse benzylic and aliphatic primary alcohols, including 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural (HMF) and substrates bearing heterocycles and other important functional groups. In many cases, the desired carboxylic acid product is obtained in >90% yield. Additionally, the catalyst has been demonstrated in a continuous-flow packed-bed reactor for the oxidation of benzyl alcohol, achieving near-quantitative yield while undergoing over 30 000 turnovers.
DATA FROM OTHER SOURCES.........






Experiments: | ||||||||||||||||
|
///////////






![2D [1H,13C]-HSQC](http://mmcd.nmrfam.wisc.edu/png/expnmr_00689_6.png)
![2D [1H,13C]-HMBC](http://mmcd.nmrfam.wisc.edu/png/expnmr_00689_7.png)
![2D [1H,1H]-COSY](http://mmcd.nmrfam.wisc.edu/png/expnmr_00689_8.png)
No comments:
Post a Comment