5-Methylfurfurylamine
CAS: 14003-16-8
((5-Methyl-2-furyl)methylamine)
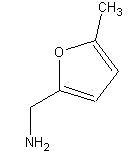
5-methylfurfurylamine also contains both C=C double bonds and C-O bonds. As in piperonal, the two carbons attached to the oxygen in the 5-methylfurfurylamine molecule could fall in the 145 to 160 ppm range.
The carbon in the methyl group falls within the alkane chemical shift range of 0 to 35 ppm. A peak at 14 ppm can be seen below. Alkenes have C NMR shifts between 100 and 150 ppm. The two alkene carbons have peaks at about 106 ppm.
C-N bonds can have a chemical shift between 45 and 55 ppm. This shift is greater in the 5-methylfurfurylamine molecule because the carbon is attached to another carbon with a C=C and a C-O bond. A peak can be seen at 78 ppm.

DEPT

1H nmr


5-methylfurfurylamine could be synthesized by breaking the bond between the amino group and the CH2 attached to carbon number 2 of the 5-membered ring. If using bromine within this SN2 reaction, this break would result in the formation of the electrophile, 5-methylfurfurybromide, and the neutral nucleophile, ammonia. The single lone pair of the nucleophile would then attack the carbon attached directly to the halogen, bromine; and as a result, negatively charged bromine would be released. However, this would not directly result in the formation of the desired reactant, 5-methylfurfurylamine, because of the attachment of positively charged ammonia. Thus, at this point an acid-base reaction would occur with another ammonia molecule, and would result in the formation of the desired neutral reactant, 5-methylfurfurylamine.
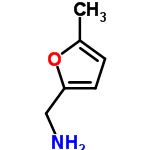
CAS: 14003-16-8
((5-Methyl-2-furyl)methylamine)

5-methylfurfurylamine also contains both C=C double bonds and C-O bonds. As in piperonal, the two carbons attached to the oxygen in the 5-methylfurfurylamine molecule could fall in the 145 to 160 ppm range.
The carbon in the methyl group falls within the alkane chemical shift range of 0 to 35 ppm. A peak at 14 ppm can be seen below. Alkenes have C NMR shifts between 100 and 150 ppm. The two alkene carbons have peaks at about 106 ppm.
C-N bonds can have a chemical shift between 45 and 55 ppm. This shift is greater in the 5-methylfurfurylamine molecule because the carbon is attached to another carbon with a C=C and a C-O bond. A peak can be seen at 78 ppm.
DEPT
1H nmr
5-methylfurfurylamine could be synthesized by breaking the bond between the amino group and the CH2 attached to carbon number 2 of the 5-membered ring. If using bromine within this SN2 reaction, this break would result in the formation of the electrophile, 5-methylfurfurybromide, and the neutral nucleophile, ammonia. The single lone pair of the nucleophile would then attack the carbon attached directly to the halogen, bromine; and as a result, negatively charged bromine would be released. However, this would not directly result in the formation of the desired reactant, 5-methylfurfurylamine, because of the attachment of positively charged ammonia. Thus, at this point an acid-base reaction would occur with another ammonia molecule, and would result in the formation of the desired neutral reactant, 5-methylfurfurylamine.
No comments:
Post a Comment